765090
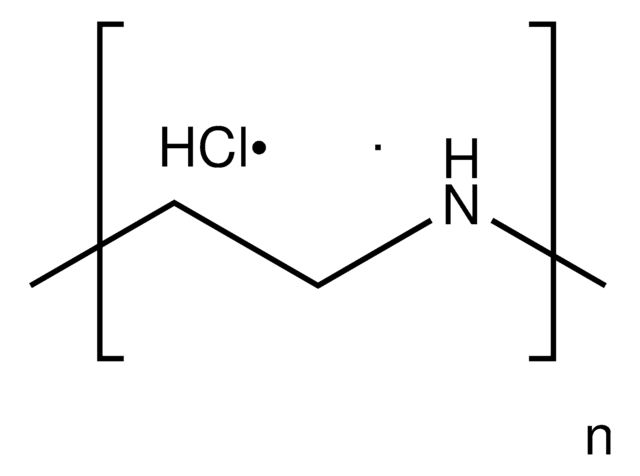
Polyethylenimine, linear
average Mn 10,000, PDI ≤1.3
Synonym(s):
PEI
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
solid
mol wt
average Mn 10,000
mp
48-53 °C
PDI
≤1.3
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
N1CC1
InChI
1S/C2H5N/c1-2-3-1/h3H,1-2H2
InChI key
NOWKCMXCCJGMRR-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Delivery of Nucleic Acids Using Polymers
Professor Yoshiki Katayama (Kyushu University, Japan) discusses recent advances in drug delivery systems and strategies that exploit the EPR effect, with a special focus on stimuli-responsive systems based on novel materials.
Wide range of functional polymers for biomedical applications have been synthesized and structurally characterized. Several classes of polymers including biodegradable polymers, hydrophilic & amphiphilic polymers, and stimuli responsive polymers have been prepared using controlled and directed functionalization via "living" polymerization such as RAFT, ionic and ring opening polymerization. Selected polymers have been studied for their structure-properties relationship. "
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service