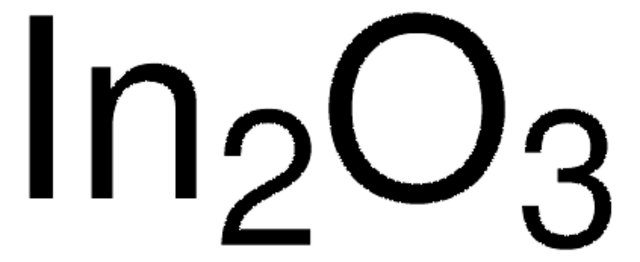632317
Indium(III) oxide
nanopowder, <100 nm particle size (TEM), 99.9% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
Diindium trioxide, Indium sesquioxide
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
In2O3
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
277.63
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352302
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
vapor pressure
<0.01 mmHg ( 25 °C)
Quality Level
Assay
99.9% trace metals basis
form
nanopowder
reaction suitability
reagent type: catalyst
core: indium
particle size
<100 nm (TEM)
density
7.18 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
O=[In]O[In]=O
InChI
1S/2In.3O
InChI key
SHTGRZNPWBITMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Indium(III)oxide is a versatile compound with significant applications in electronics,optics, and materials science. It is widely employed in the synthesis of transparentconducting oxides (TCOs), particularly for flat-panel displays, and solarcells, due to its electrical conductivity and optical transparency. Insemiconductor technology, it is used for making indium tin oxide (ITO),enhancing the performance of electronic devices, and is sensitive to variousgases, making it suitable for gas sensing applications, particularly indetecting hazardous gases.
Application
- Amine Functionalized Surface Frustrated Lewis Pairs for CO2 Photocatalysis: Discusses the enhancement of photocatalytic performance for CO2 reduction using indium oxide hydroxide with amine-functionalized surface frustrated Lewis pairs (Q Guan et al., 2024).
- Enhancing Gas Sensing Performance through UV Photoexcitation: Explores the improvement of room-temperature gas sensing capabilities of metal oxide semiconductor chemiresistors, including indium(III) oxide, by 400 nm UV photoexcitation (S Paul et al., 2024).
- Indium(III) Complexes in Industry and Nanoparticle Synthesis: Reviews the use of trivalent indium complexes as catalysts and precursors for various industrial applications and the synthesis of nanoparticles like indium oxide (TO Ajiboye et al., 2024).
- Ag/In2O3 Inverse Opal Synthesis: Details the synthesis and perspectives of silver/indium oxide inverse opal structures, highlighting their potential in semiconductor applications due to their optical properties (AV Lyutova et al., 2024).
- Photocatalytic Generation of Hydroxyl Radicals and Manganese Species: Investigates the use of indium oxide in enhancing the photocatalytic performance of permanganate for efficient micropollutant removal under visible light (J Li et al., 2024).
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Xiaoyun Li et al.
Environmental science & technology, 46(10), 5528-5534 (2012-04-12)
Perfluorooctanoic acid (C(7)F(15)COOH, PFOA) has increasingly attracted worldwide concerns due to its global occurrence and resistance to most conventional treatment processes. Though TiO(2)-based photocatalysis is strong enough to decompose most organics, it is not effective for PFOA decomposition. We first
Xuming Zou et al.
ACS nano, 7(1), 804-810 (2012-12-12)
In recent years, In(2)O(3) nanowires (NWs) have been widely explored in many technological areas due to their excellent electrical and optical properties; however, most of these devices are based on In(2)O(3) NW field-effect transistors (FETs) operating in the depletion mode
Dongjin Lee et al.
Sensors (Basel, Switzerland), 11(10), 9300-9312 (2011-12-14)
We report a conductometric nanoparticle biosensor array to address the significant variation of electrical property in nanomaterial biosensors due to the random network nature of nanoparticle thin-film. Indium oxide and silica nanoparticles (SNP) are assembled selectively on the multi-site channel
K H L Zhang et al.
Journal of physics. Condensed matter : an Institute of Physics journal, 23(33), 334211-334211 (2011-08-05)
Epitaxial films of In(2)O(3) have been grown on Y-stabilised ZrO(2)(111) substrates by molecular beam epitaxy over a range of thicknesses between 35 and 420 nm. The thinnest films are strained, but display a 'cross-hatch' morphology associated with a network of
Mareike V Hohmann et al.
Journal of physics. Condensed matter : an Institute of Physics journal, 23(33), 334203-334203 (2011-08-05)
The ionization potentials of In(2)O(3) films grown epitaxially by magnetron sputtering on Y-stabilized ZrO(2) substrates with (100) and (111) surface orientation are determined using photoelectron spectroscopy. Epitaxial growth is verified using x-ray diffraction. The observed ionization potentials, which directly affect
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service