T5393
Anti-Mouse IgG (whole molecule)−TRITC antibody produced in goat
IgG fraction of antiserum, buffered aqueous solution
Synonym(s):
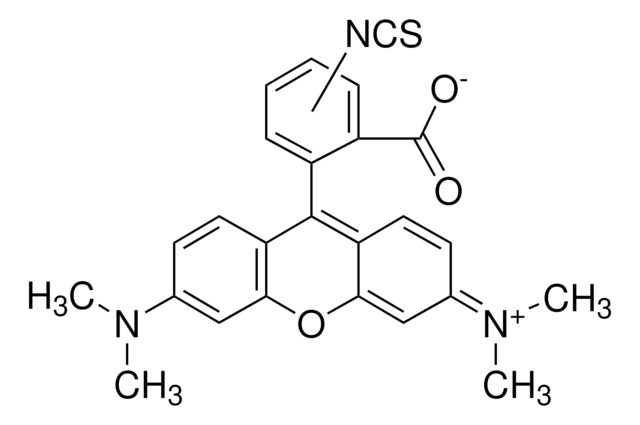
Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (whole molecule)−Tetramethylrhodamine isothiocyanate
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
goat
Quality Level
conjugate
TRITC conjugate
antibody form
IgG fraction of antiserum
antibody product type
secondary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
technique(s)
direct immunofluorescence: 1:64
storage temp.
2-8°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
General description
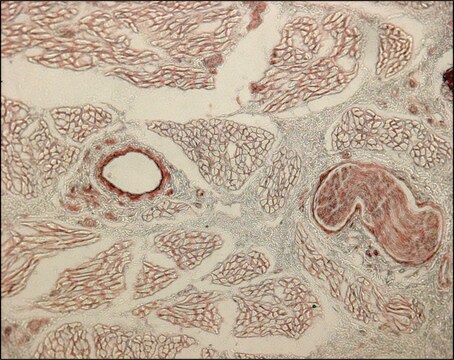
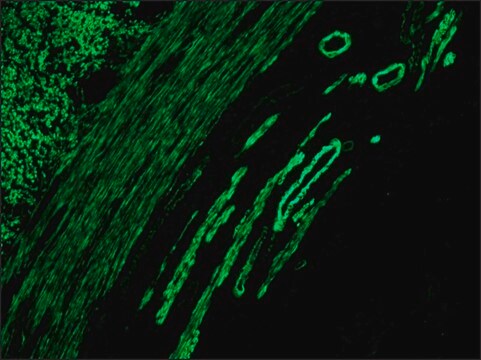
Anti-Mouse IgG (whole molecule)-TRITC antibody is specific for mouse IgG and all subclasses, it cross reacts with mouse IgA and IgM. Antibody purification is by ion exchange chromatography after which it is conjugated to crystalline tetramethylrhodamine isothiocyanate (TRITC).
Specificity
Immunogen
Application
Physical form
Disclaimer
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service