I5654
IgG3, Kappa from human myeloma plasma
purified immunoglobulin, >90% (microfluidic capillary gel electrophoresis)
Synonym(s):
Human IgG3-κ
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
human
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
Assay
>90% (microfluidic capillary gel electrophoresis)
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
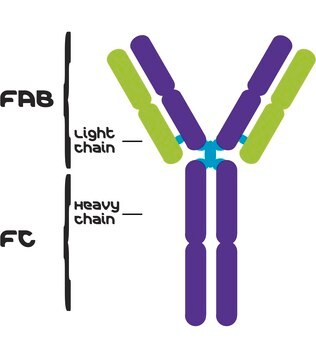
IgG antibody subtype is the most abundant serum immunoglobulins of the immune system. It is secreted by B cells and is found in blood and extracellular fluids and provides protection from infections caused by bacteria, fungi and viruses. Maternal IgG is transferred to fetus through the placenta that is vital for immune defence of the neonate against infections. IgG3 is the has a unique extended hinge region conferring greater flexibility
Human myeloma IgG3, κ is purified from human plasma by fractionation, ion-exchange, and affinity chromatography procedures.
Human myeloma IgG3, κ is purified from human plasma by fractionation, ion-exchange, and affinity chromatography procedures.
Application
IgG3, kappa from human myeloma plasma has been used to determine the trisulfide levels in commercial therapeutic IgG1 antibodies and in human myeloma IgG1, IgG2, IgG3 and IgG4 antibodies.
The purified IgG3, κ may be used as an immunoglobulin calibrator, reference antigen, blocking agent or coating protein in a variety of immunoassays including ELISA, dot-blot immunobinding, Western immunoblotting, immunodiffusion, immunoelectrophoresis, hemagglutination, and cell-binding assays. Human myeloma IgG3 was for in flow cytometry in CHO cells.
Physical form
Solution in 20 mM tris buffered saline, pH 8.0.
Analysis Note
The purity and identity are determined by immunoelectrophoresis, indirect ELISA and SDS-PAGE.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Characterization of trisulfide modification in antibodies
Gu S, et al.
Analytical Biochemistry, 400(1), 89-98 (2010)
Rangaiah Shashidharamurthy et al.
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), 183(12), 8216-8224 (2009-12-17)
CD32A, the major phagocytic FcgammaR in humans, exhibits a polymorphism in the ligand binding domain. Individuals homozygous for the R allelic form of CD32A (CD32A(R) allele) are more susceptible to bacterial infections and autoimmune diseases as compared with H allelic
David R Martinez et al.
Cell, 178(1), 190-201 (2019-06-18)
The placental transfer of maternal IgG is critical for infant protection against infectious pathogens. However, factors that modulate the placental transfer of IgG remain largely undefined. HIV-infected women have impaired placental IgG transfer, presenting a unique "disruption model" to define
Masayuki Hirano et al.
Nature immunology, 8(7), 762-771 (2007-06-15)
Because functional analysis of Fc receptors (FcRs) relies heavily on mouse models, the identification of another Fcgamma receptor is particularly noteworthy. We demonstrate that FcgammaRIV, identified here as the mouse ortholog of primate FcgammaRIII, required association of the FcR gamma-chain
S Hashira et al.
Pediatrics international : official journal of the Japan Pediatric Society, 42(4), 337-342 (2000-09-15)
Maternal immunoglobulin G (IgG), transferred across the placenta to the fetus during intrauterine life, is an important component of the neonatal immunological defence mechanisms against infection. There is controversy with respect to differences in placental transfer of the different IgG
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service