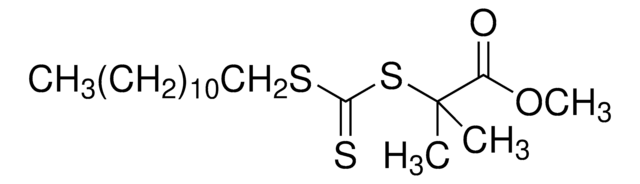
900152
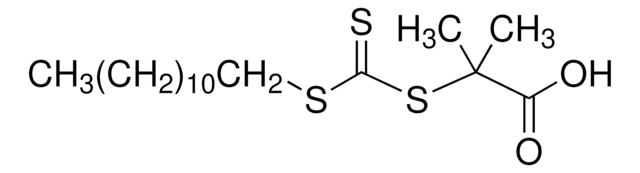
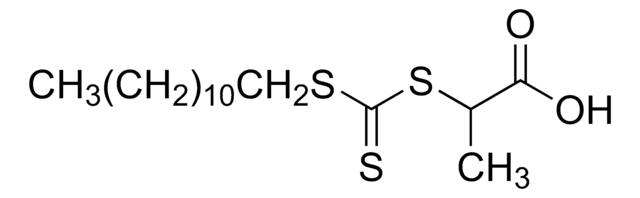
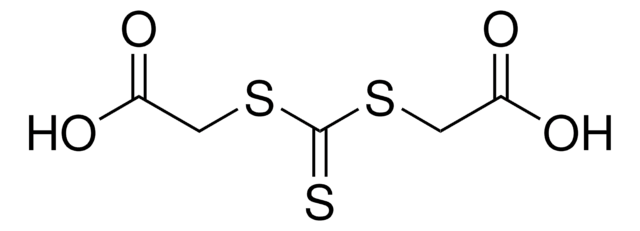
2-[[(2-Carboxyethyl)sulfanylthiocarbonyl]-sulfanyl]propanoic acid
About This Item
Recommended Products
General description
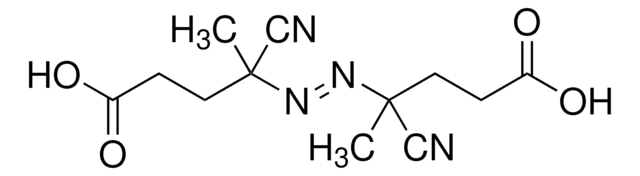
- A stable, trithiocarbonate chain transfer agent (CTA), also referred to as a RAFT agent, which can control chain growth in free radical polymerization producing polymers with well-defined molecular weights and low polydispersities.
- 2-(2-Carboxyethylsulfanylthiocarbonylsulfanyl)propionic acid may be used to control homo- and co-polymerization of acrylic acid, acrylates, acrylamides, styrenes, methacrylates, and methacrylamides. It is soluble in aqueous and organic media (amphiphilic).
Caution
Legal Information
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
The supply of low cost, high purity and effective Reversible addition−fragmentation chain-transfer (RAFT) Agents is the essential element in the industrial implementation of RAFT polymerization technology.
The modification of biomacromolecules, such as peptides and proteins, through the attachment of synthetic polymers has led to a new family of highly advanced biomaterials with enhanced properties.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service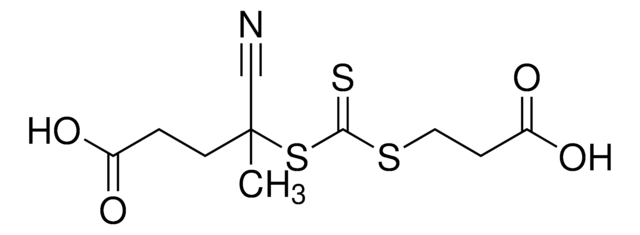
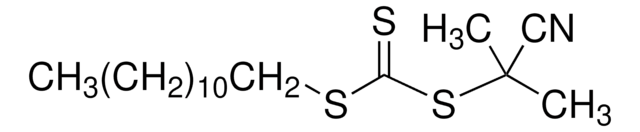
![4-Cyano-4-[(dodecylsulfanylthiocarbonyl)sulfanyl]pentanoic acid 97% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/204/925/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af/640/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af.png)