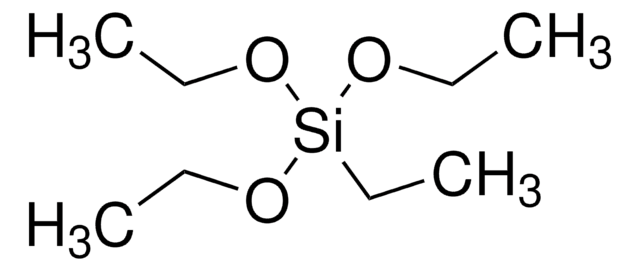
440175
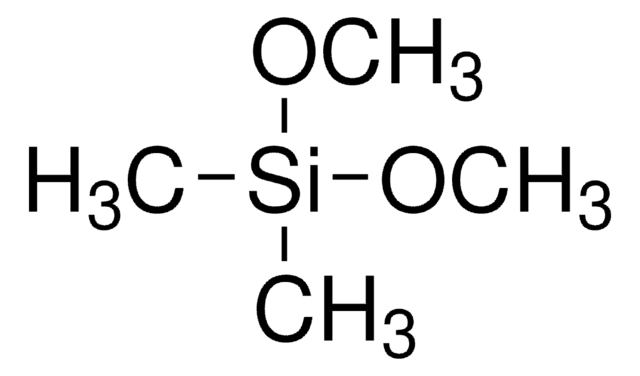
Trimethoxymethylsilane
95%
Synonym(s):
MTMS, Methyltrimethoxysilane
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
95%
form
liquid
impurities
3% methyl alcohol
refractive index
n20/D 1.371 (lit.)
bp
102-104 °C (lit.)
density
0.955 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
CO[Si](C)(OC)OC
InChI
1S/C4H12O3Si/c1-5-8(4,6-2)7-3/h1-4H3
InChI key
BFXIKLCIZHOAAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
Application
- Monolithic silica columns with various skeleton sizes for capillary liquid chromatography.
- Ionogels, where an ionic liquid is confined within silica-derived networks.
- Monolithic silica aerogels via acid-base sol-gel polymerization.
- Hydrophobic, flexible, and ultralightweight silylated nanocellulose sponges for the selective removal of oil from water.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Flam. Liq. 2
Storage Class Code
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
48.2 °F
Flash Point(C)
9 °C
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Advances in materials have often been led by the development of new synthetic methods that provide control over size, morphology and structure. The preparation of materials in a scalable and continuous manner is critical when development moves beyond lab-scale quantities.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service