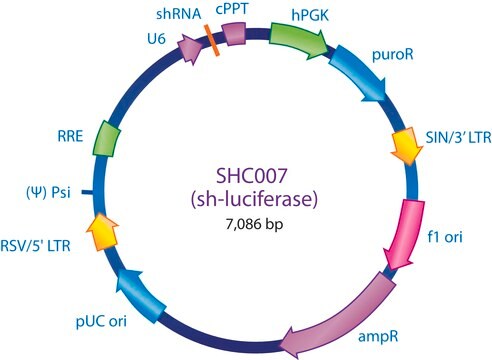
SHC332
MISSION® 3X LacO Inducible Non-Target shRNA Control Plasmid DNA
Does not target any known genes
Synonym(s):
MISSION® Control Vectors
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
product line
MISSION®
concentration
500 ng/μL in TE buffer; DNA (10μg of plasmid DNA)
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Sigma® is proud to offer IPTG-inducible vectors as the latest development from our continued partnership in TRC.
The pLKO vector has been redesigned to contain a LacI (repressor) and a modified human U6 shRNA promoter with LacO (operator) sequences. In the absence of IPTG (isopropyl-Β-D-thio-galactoside), an analogue of lactose, LacI binds to LacO preventing expression of the shRNA. When IPTG is present, the allosteric LacI repressor changes conformation, releasing itself from lacO modified human U6 promoter, and subsequently allows expression of the shRNA.
We are proud to offer two different IPTG inducible vectors for your research. The preferred inducible vector, pLKO_IPTG_3xLacO, contains three lac operon sequences (two in the U6 promoter and one 3′ of the promoter) affording both tight regulation and great gene silencing. Whereas, the pLKO_IPTG_1xLacO vector contains a single lac operon sequence in the U6 promoter, which allows for an advantage to shRNA expression, but looser control of the promoter when not induced.
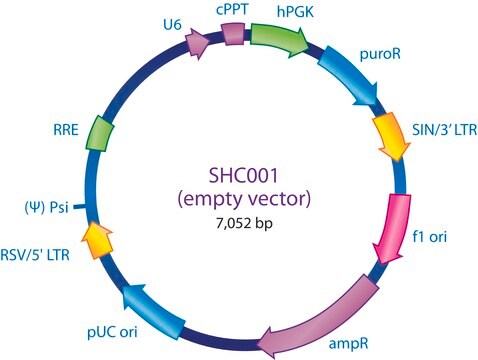
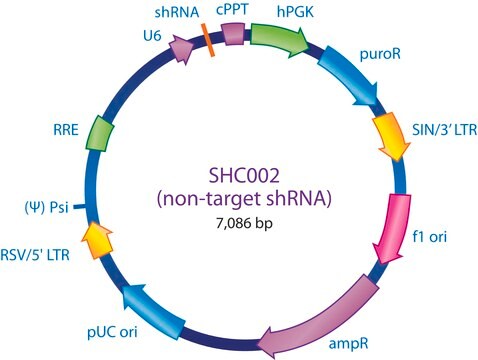
The MISSION® 3X LacO Inducible Non-Target shRNA Control is a lentivirus plasmid vector. The vector contains an shRNA insert that does not target any known genes, making it useful as a negative control in experiments using the MISSION inducible shRNA library clones. This allows one to examine the effect of transfection of a short-hairpin on gene expression and interpret the knockdown effect seen with shRNA clones. Ampicillin and puromycin antibiotic resistance genes provide selection in bacterial or mammalian cells respectively. In addition, self-inactivating replication incompetent viral particles can be produced in packaging cells (HEK293T) by co-transfection with compatible packaging plasmids. The 1X LacO Inducible Non-Target shRNA Control is provided as 10 μg of plasmid DNA in Tris-EDTA (TE) buffer at a concentration of 500 ng/μl.
The pLKO vector has been redesigned to contain a LacI (repressor) and a modified human U6 shRNA promoter with LacO (operator) sequences. In the absence of IPTG (isopropyl-Β-D-thio-galactoside), an analogue of lactose, LacI binds to LacO preventing expression of the shRNA. When IPTG is present, the allosteric LacI repressor changes conformation, releasing itself from lacO modified human U6 promoter, and subsequently allows expression of the shRNA.
We are proud to offer two different IPTG inducible vectors for your research. The preferred inducible vector, pLKO_IPTG_3xLacO, contains three lac operon sequences (two in the U6 promoter and one 3′ of the promoter) affording both tight regulation and great gene silencing. Whereas, the pLKO_IPTG_1xLacO vector contains a single lac operon sequence in the U6 promoter, which allows for an advantage to shRNA expression, but looser control of the promoter when not induced.
The MISSION® 3X LacO Inducible Non-Target shRNA Control is a lentivirus plasmid vector. The vector contains an shRNA insert that does not target any known genes, making it useful as a negative control in experiments using the MISSION inducible shRNA library clones. This allows one to examine the effect of transfection of a short-hairpin on gene expression and interpret the knockdown effect seen with shRNA clones. Ampicillin and puromycin antibiotic resistance genes provide selection in bacterial or mammalian cells respectively. In addition, self-inactivating replication incompetent viral particles can be produced in packaging cells (HEK293T) by co-transfection with compatible packaging plasmids. The 1X LacO Inducible Non-Target shRNA Control is provided as 10 μg of plasmid DNA in Tris-EDTA (TE) buffer at a concentration of 500 ng/μl.
Application
To see more application data, protocols, vector maps visit sigma.com/shrna.
Legal Information
Use of this product is subject to one or more license agreements. For details, please see http://sigmaaldrich.com/missionlicense.
MISSION is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Sigma is a registered trademark of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC
recommended
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documents section.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Daniel J Puleston et al.
Cell metabolism, 30(2), 352-363 (2019-05-28)
How cells adapt metabolism to meet demands is an active area of interest across biology. Among a broad range of functions, the polyamine spermidine is needed to hypusinate the translation factor eukaryotic initiation factor 5A (eIF5A). We show here that
Polyamines Control eIF5A Hypusination, TFEB Translation, and Autophagy to Reverse B Cell Senescence.
Hanlin Zhang et al.
Molecular cell, 76(1), 110-125 (2019-09-03)
Failure to make adaptive immune responses is a hallmark of aging. Reduced B cell function leads to poor vaccination efficacy and a high prevalence of infections in the elderly. Here we show that reduced autophagy is a central molecular mechanism
Swapna Aravind Gudipaty et al.
Molecular and cellular biology, 35(22), 3810-3828 (2015-09-02)
Transcription elongation programs are vital for the precise regulation of several biological processes. One key regulator of such programs is the P-TEFb kinase, which phosphorylates RNA polymerase II (Pol II) once released from the inhibitory 7SK small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service