ML0015
Aspartate Metabolite Library
Synonym(s):
Aspartic acid Metabolite Library
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352209
NACRES:
NA.25
Recommended Products
General description
Aspartic acid (or aspartate) is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is naturally synthesized by mammals. Aspartate presents many biochemical roles:
In the L-conformation, aspartic acid is a building block in the production of proteins, as well as aiding in many bodily functions, including the urea cycle, gluconeogenesis, and Krebs Cycle, a process that generates adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Aspartic acid also works as a neurotransmitter. The D-Aspartate conformation is linked to neurogenesis and endocrine systems.
In the L-conformation, aspartic acid is a building block in the production of proteins, as well as aiding in many bodily functions, including the urea cycle, gluconeogenesis, and Krebs Cycle, a process that generates adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Aspartic acid also works as a neurotransmitter. The D-Aspartate conformation is linked to neurogenesis and endocrine systems.
Application
The Aspartate Metabolite Library is a kit that contains a selection of 23 metabolite involved in Aspartate metabolism.These may be used for general research, as reagents or as reference compounds in analytical procedures.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Aspartate roles and metabolites:
- Aspartate is synthesized by transamination of oxaloacetate through the actions of Aspartate aminotransferase and pyridoxal 5′- phosphate. Aspartyl-tRNA synthase can then couple the aspartate to aspartyl tRNA for protein synthesis.
- Aspartate carries the reducing equivalents in the mitochondrial Malate-Aspartate shuttle, which uses the ready interconversion of aspartate and oxaloacetate.
- N-acetylaspartate synthase, present in the cytoplasm, converts aspartate to N-acetylaspartate, a brain metabolite that regulates dopamine.
- Asparagine is biosynthesized by Asparagine synthetase from aspartate, glutamine, and ATP. Asparagine is involved in the metabolic control of cell functions in nerve and brain tissue.
- Arginosuccinic acid is synthesized from aspartate, citrulline and ATP through the action of Argininosuccinate synthase, one of the enzymes of the urea cycle. In this metabolic pathway, neurotoxic ammonia, produced by protein catabolism, is converted into urea in the liver.
- Fumaric acid is synthesized from Argininosuccinic acid via an Argininosuccinate lyase, which is an enzyme in the Citric Acid Cycle.
- Inosinic acid, aspartic acid and GTP are interconverted to GDP and AMP by the Adenylosuccinate synthetase isozyme 1. This process is involved in the purine nucleotide cycle which regulates nucleotides levels in various tissues.
- Aspartate transcarbamoylase catalyzes the synthesis of N-carbamoyl-L-aspartate from carbamoyl phosphate and aspartate that are involved in the de novo biosynthesis of pyrimidines.
- Beta alanine is formed by decarboxylation of aspartate by Glutamate decarboxylase 1 in the cytoplasm.
- L-aspartate is converted to D-aspartate through the action of a D-aspartate racemase. D-aspartate contributes to the synthesis and release of glucocorticoids, prolactin, oxytocin, and steroids. D-aspartate plays an important role in the brain activity of mammals.
Components
Contains 10 mg each of Aspartate metabolism metabolite standards packaged individually.
Kit Components Also Available Separately
Product No.
Description
SDS
- A2252Adenosine 5′-monophosphate monohydrate, from yeast, ≥97%SDS
- A2383Adenosine 5′-triphosphate disodium salt hydrate, Grade I, ≥99%, from microbialSDS
- A5707Argininosuccinic acid disodium salt hydrate, ≥80%SDS
- 146064β-Alanine, 99%SDS
- C4135Carbamyl phosphate disodium salt, ≥80%SDS
- C7629L-Citrulline, ≥98% (TLC)SDS
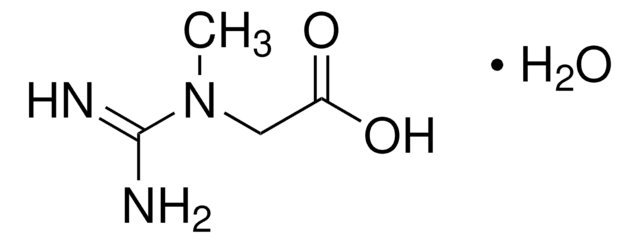
- 219096D-Aspartic acid, ReagentPlus®, 99%SDS
- F6625Flavin adenine dinucleotide disodium salt hydrate, ≥95% (HPLC), powderSDS
- 47910Fumaric acid, ≥99.0% (T)SDS
- G7252Guanosine 5′-diphosphate tris salt from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Type VI, ≥92.5%SDS
- G9002Guanosine 5′-triphosphate tris salt, ≥93% (HPLC), powderSDS
- I2879Inosine 5′-monophosphate from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, ≥98%SDS
- A5006L-Arginine, reagent grade, ≥98%SDS
- A0884L-Asparagine, ≥98% (HPLC)SDS
- 11189L-Aspartic acid, BioUltra, ≥99.5% (T)SDS
- G1251L-Glutamic acid, ReagentPlus®, ≥99% (HPLC)SDS
- G3126L-Glutamine, ReagentPlus®, ≥99% (HPLC)SDS
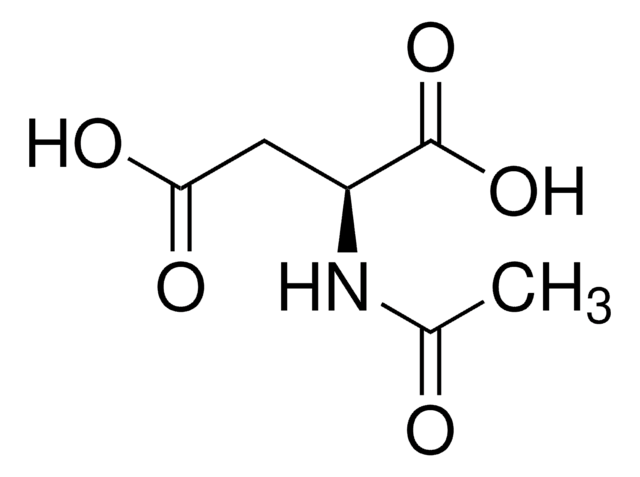
- 00920N-Acetyl-L-aspartic acid, ≥99.0% (T)SDS
- O4126Oxaloacetic acid, ≥97% (HPLC)SDS
- K1750α-Ketoglutaric acid, ≥98.5% (NaOH, titration)SDS
- P9255Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate hydrate, ≥98%SDS
- P8010Sodium pyrophosphate tetrabasic, ≥95%SDS
- 69037Ureidosuccinic acid, 98.0-102.0% (T)SDS
See All (23)
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Sorry, we don't have COAs for this product available online at this time.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Pyrimidine Biosynthesis
Lennarz W J, et al.
Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry, 600-605 (2004)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service