MAK133
ADP Assay Kit
sufficient for 100 assays (bioluminescent)
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12161503
NACRES:
NA.84
Recommended Products
usage
sufficient for 100 assays (bioluminescent)
detection method
chemiluminescent
relevant disease(s)
hematological disorder; cancer
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) is a nucleoside that plays a critical role in energy transfer reactions. ADP is produced from adenosine triphosphate via the action of ATPases. ADP also plays a critical role in platelet function. ADP, stored in plate-dense granules, is released upon platelet activation where it acts on purinergic receptors to mediate intracellular signaling and platelet aggregation.
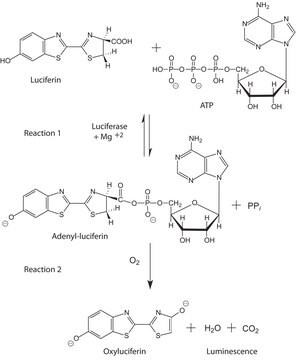
The ADP Assay kit provides a simple and direct procedure for measuring ADP levels in cells and other biological samples. The assay involves two steps. In the first step, the working reagent lyses cells to release ATP and ADP. In the presences of luciferse, ATP immediately reacts with the Substrate (D-luciferin) to produce light. The light intensity is a direct measure of the intracellular ATP concentration and is stable over several minutes.
In the second step, the ADP is converted to ATP through an enzyme reaction. This newly formed ATP then reacts with the D-luciferin as in the first step. The second light intensity measured represents the total ADP and ATP concentration in the sample.
The ADP Assay kit provides a simple and direct procedure for measuring ADP levels in cells and other biological samples. The assay involves two steps. In the first step, the working reagent lyses cells to release ATP and ADP. In the presences of luciferse, ATP immediately reacts with the Substrate (D-luciferin) to produce light. The light intensity is a direct measure of the intracellular ATP concentration and is stable over several minutes.
In the second step, the ADP is converted to ATP through an enzyme reaction. This newly formed ATP then reacts with the D-luciferin as in the first step. The second light intensity measured represents the total ADP and ATP concentration in the sample.
Suitability
Suitable for the detection of ADP in cells, tissue and other biological samples.
Principle
The ADP Assay kit provides a simple and direct procedure for measuring ADP levels in cells and other biological samples. The assay involves two steps. In the first step, the working reagent lyses cells to release ATP and ADP. In the presences of luciferse, ATP immediately reacts with the substrate (D-luciferin) to produce light. The light intensity is a direct measure of the intracellular ATP concentration and is stable over several minutes.
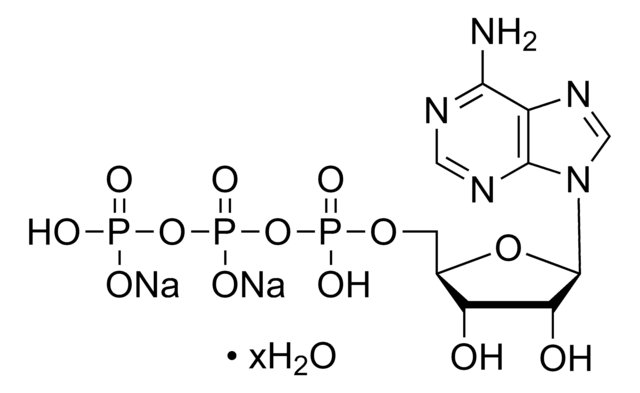
Luciferase ATP + D-Luciferin + O2 → oxyluciferin + AMP + PPi + CO2 + light
In the second step, the ADP is converted to ATP through an enzyme reaction. This newly formed ATP then reacts with the D-luciferin as in the first step. The second light intensity measured represents the total ADP and ATP concentration in the sample.
Luciferase ATP + D-Luciferin + O2 → oxyluciferin + AMP + PPi + CO2 + light
In the second step, the ADP is converted to ATP through an enzyme reaction. This newly formed ATP then reacts with the D-luciferin as in the first step. The second light intensity measured represents the total ADP and ATP concentration in the sample.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 3 - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
The membrane ATPase of Escherichia coli: I. Ion dependence and ATP-ADP exchange reaction.
Roisin M P and Kepes A
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - Bioenergetics, 275(3), 333-346 (1972)
Hongshan Ge et al.
Molecular and cellular endocrinology, 443, 128-137 (2017-01-17)
To explore the roles of mitochondrial Uncoupling Protein 2 (UCP2) in cumulus cells (CCs), human CCs were cultured in vitro, and the UCP2 was inhibited by treatment with Genipin, a special UCP inhibitor, or by RNA interference targeting UCP2. No significant
Sepinoud Firouzmand et al.
Neurourology and urodynamics, 39(3), 926-934 (2020-02-13)
To characterize purinergic signaling in overactive bladder (OAB). Mucosal biopsies were taken by flexible cystoscopy from patients with storage symptoms referred to Urology Departments of collaborating hospitals. Immunohistochemistry (n = 12) and Western blot analysis (n = 28) were used to establish the qualitative
Aggregation of blood platelets by adenosine diphosphate and its reversal.
Born G V R
Nature, 194(4832), 927-929 (1962)
Yingzhong Li et al.
Nature communications, 11(1), 4837-4837 (2020-09-26)
ATP synthesis and thermogenesis are two critical outputs of mitochondrial respiration. How these outputs are regulated to balance the cellular requirement for energy and heat is largely unknown. Here we show that major facilitator superfamily domain containing 7C (MFSD7C) uncouples
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service