All Photos(1)
About This Item
CAS Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.77
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥98%
form
ethanol solution
mol wt
apparent mol wt 323.5
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
CCCCC\C=C/C\C=C/CCCCCCCC(=O)NCCO
InChI
1S/C20H37NO2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-20(23)21-18-19-22/h6-7,9-10,22H,2-5,8,11-19H2,1H3,(H,21,23)/b7-6-,10-9-
InChI key
KQXDGUVSAAQARU-HZJYTTRNSA-N
Biochem/physiol Actions
Linoleoyl ethanolamide (LE), a fatty acid ethanolamide, is present in sake lees. It possesses anti-inflammatory effects by preventing nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling. LE is considered a beneficial therapeutic agent for contact dermatitis.
Preparation Note
To change the solvent, evaporate the ethanol under a gentle stream of nitrogen and immediately add the solvent of choice.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Liq. 2
Storage Class Code
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
57.2 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
14 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Thi Ai Diep et al.
FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, 25(2), 765-774 (2010-10-21)
This study was undertaken to investigate the link between dietary fat content and intestinal levels of anorectic N-acylethanolamines (NAEs), including oleoylethanolamide (OEA), palmitoylethanolamide (PEA), and linoleoylethanolamide (LEA). Male rats were fed high-fat diets (HFDs) with variable percentages of fat [20-45%
The endogenous cannabimimetic eicosanoid, anandamide, induces arachidonate release in J774 mouse macrophages.
V Di Marzo et al.
Advances in experimental medicine and biology, 407, 341-346 (1997-01-01)
Harald S Hansen et al.
Biochemical pharmacology, 78(6), 553-560 (2009-05-06)
Anandamide and the other N-acylethanolamines, e.g. oleoylethanolamide (OEA), palmitoylethanolamide (PEA), and linoleoylethanolamide (LEA), may be formed by several enzymatic pathways from their precursors, which are the N-acylated ethanolamine phospholipids. The exact enzymatic pathways involved in their biosynthesis in specific tissues
Two new unsaturated fatty acid ethanolamides in brain that bind to the cannabinoid receptor.
L Hanus et al.
Journal of medicinal chemistry, 36(20), 3032-3034 (1993-10-01)
Joe Palandra et al.
Journal of chromatography. B, Analytical technologies in the biomedical and life sciences, 877(22), 2052-2060 (2009-06-19)
A sensitive and selective liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC\MS\MS) method has been developed for the simultaneous quantification in human plasma of the endocannabinoid anandamide (AEA) and three other related ethanolamides, linoleoyl ethanolamide (LEA), oleoyl ethanolamide (OEA), and palmitoyl ethanolamide
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service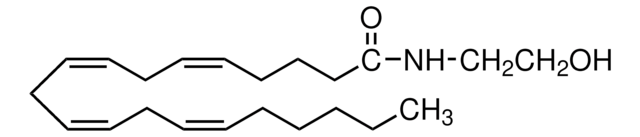




![Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid] natural origin](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/129/476/7d1c924b-f644-4889-a2d6-d7a923ce382c/640/7d1c924b-f644-4889-a2d6-d7a923ce382c.png)



