D4893
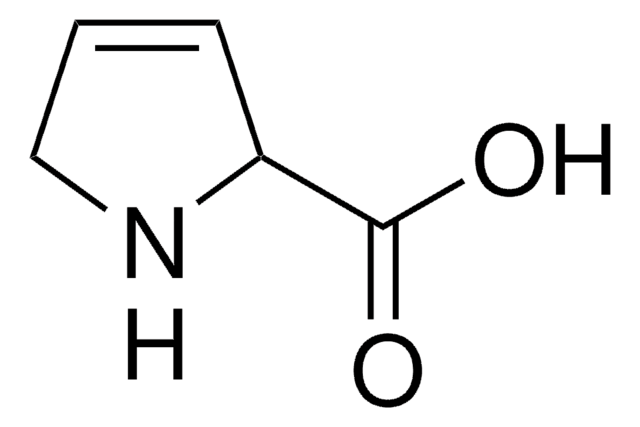
3,4-Dehydro-L-proline
≥98% (TLC), suitable for ligand binding assays
Synonym(s):
(S)-3-Pyrroline-2-carboxylic acid, 3,4-Didehydro-L-proline
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C5H7NO2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
113.11
Beilstein:
5376764
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352209
eCl@ss:
32160406
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.26
Recommended Products
Product Name
3,4-Dehydro-L-proline,
Assay
≥98% (TLC)
Quality Level
form
powder
technique(s)
ligand binding assay: suitable
color
white
mp
248-250 °C
application(s)
peptide synthesis
SMILES string
OC(=O)[C@H]1NCC=C1
InChI
1S/C5H7NO2/c7-5(8)4-2-1-3-6-4/h1-2,4,6H,3H2,(H,7,8)/t4-/m0/s1
InChI key
OMGHIGVFLOPEHJ-BYPYZUCNSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
3,4-Dehydro-L-proline acts a prolyl-t-RNA synthetase.
Biochem/physiol Actions
3,4-Dehydro-L-proline is used as a substrate and inhibitor of various enzymes. 3,4-Dehydro-L-proline may be used to inhibit extensin biosynthesis. 3,4-Dehydro-L-proline is a alternate substrate of the amino acid oxidase, NikD. 3,4-Dehydro-L-proline inhibits collagen secretion by chondorcytes.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Acute respiratory failure (1985)
Chunxiang Xu et al.
BMC plant biology, 11, 38-38 (2011-02-26)
Hydroxyproline rich glycoproteins (HRGPs) are implicated to have a role in many aspects of plant growth and development but there is limited knowledge about their localization and function during somatic embryogenesis of higher plants. In this study, the localization and
Annick Méjean et al.
Biochemistry, 49(1), 103-113 (2009-12-04)
Anatoxin-a and homoanatoxin-a are two potent cyanobacterial neurotoxins. We recently reported the identification of the gene cluster responsible for the biosynthesis of these toxins in cyanobacteria and proposed a biosynthetic scheme starting from L-proline and involving three polyketide synthases for
Richard C D'Alonzo et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 277(27), 24788-24798 (2002-04-20)
Both collagenase-3 and osteocalcin mRNAs are expressed maximally during the later stages of osteoblast differentiation. Here, we demonstrate that collagenase-3 mRNA expression in differentiating MC3T3-E1 cells is dependent upon the presence of ascorbic acid, is inhibited in the presence of
G Xiao et al.
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.), 11(8), 1103-1113 (1997-07-01)
Osteocalcin is a hormonally regulated calcium-binding protein made almost exclusively by osteoblasts. In normal cells, osteocalcin expression requires ascorbic acid (AA), an essential cofactor for osteoblast differentiation both in vivo and in vitro. To determine the mechanism of this regulation
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service