11631
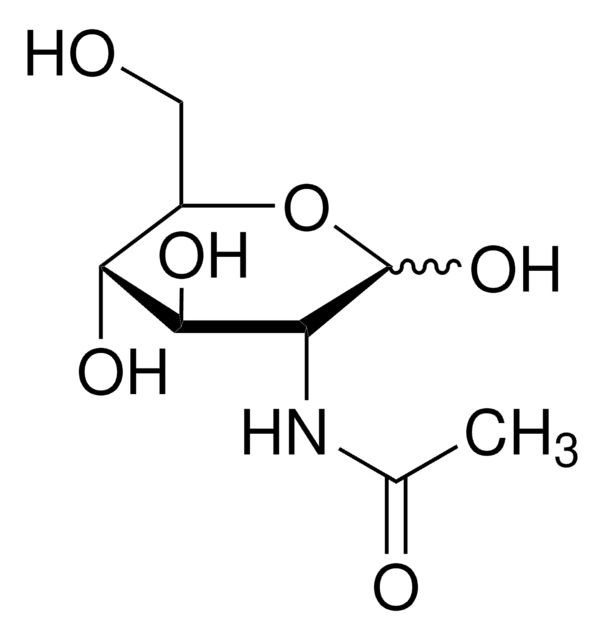
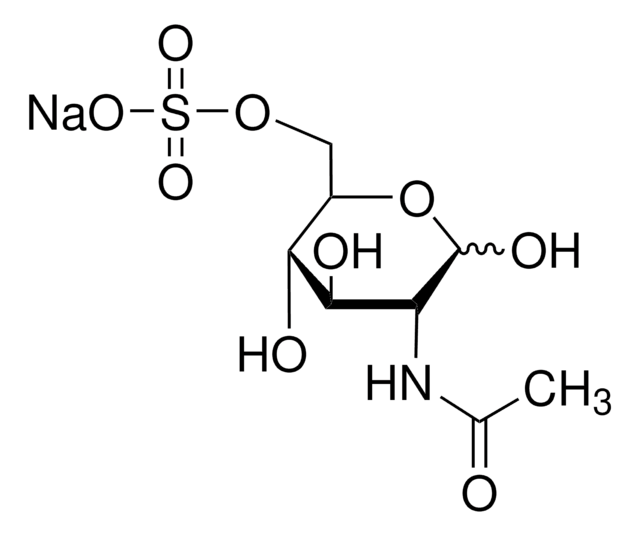
D-Glucosamine 3-sulfate
≥98.0% (TLC)
Synonym(s):
GlcN-3S
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C6H13NO8S
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
259.23
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352201
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.25
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥98.0% (TLC)
form
powder
optical activity
[α]/D 55.0±2.0
technique(s)
thin layer chromatography (TLC): suitable
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1OS(O)(=O)=O
InChI
1S/C6H13NO8S/c7-3-5(15-16(11,12)13)4(9)2(1-8)14-6(3)10/h2-6,8-10H,1,7H2,(H,11,12,13)/t2-,3-,4-,5-,6?/m1/s1
InChI key
UZUBNIPDAIVWIE-IVMDWMLBSA-N
Application
D-Glucosamine 3-sulfate (GlcN-3S) may be used as a reference in analytical analysis of the components of heparin sulfate.
Packaging
Bottomless glass bottle. Contents are inside inserted fused cone.
Other Notes
To gain a comprehensive understanding of our extensive range of Monosaccharides for your research, we encourage you to visit our Carbohydrates Category page.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
H G Garg et al.
Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 224(2), 468-473 (1996-07-16)
Heparin macromolecules inhibit vascular remodeling associated with hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Heparin's antiproliferative effect on smooth muscle cells, based on studies of synthetic pentasaccharide fragments, has been attributed to 3-O-sulfate on the internal glucosamine. To determine the role of 3-O-sulfation in
U Lindahl et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 77(11), 6551-6555 (1980-11-01)
An octasaccharide with high affinity for antithrombin was isolated after partial deaminative cleavage of heparin with nitrous acid. After conversion of the 2,5-anhydro-D-mannose end group to anhydro[1-3H]mannitol, labeled pentasaccharide was released from the octasaccharide by periodate-alkali treatment. Incubation of the
A Naggi et al.
Carbohydrate research, 336(4), 283-290 (2001-12-01)
In the framework of a project aimed at generating heparin-like sulfation patterns and biological activities in biotechnological glycosaminoglycans, different approaches have been considered for simulating the alpha(1-->4)-linked 2-O-sulfated L-iduronic acid (IdoA2SO(3))-->N,6-O-sulfated D-glucosamine (GlcNSO(3)6SO(3)) disaccharide sequences prevalent in mammalian heparins. Since
A S Edge et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 265(26), 15874-15881 (1990-09-15)
Fragmentation of the heparan sulfate chains from bovine glomerular basement membrane (GBM) by hydrazine/nitrous acid treatment followed by NaB3H4-reduction yielded a mixture of six sulfated disaccharides containing D-glucuronic (GlcUA) or L-iduronic acid (IdUA) and terminating in 2,5-anhydro[3H]mannitol (AnManH2), in addition
H Tsuda et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 271(18), 10495-10502 (1996-05-03)
Porcine intestinal heparin was extensively digested with Flavobacterium heparinase and size-fractionated by gel chromatography. Subfractionation of the hexasaccharide fraction by anion exchange high pressure liquid chromatography yielded 10 fractions. Six contained oligosaccharides derived from the repeating disaccharide region, whereas four
Articles
Glycosaminoglycans are large linear polysaccharides constructed of repeating disaccharide units.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service