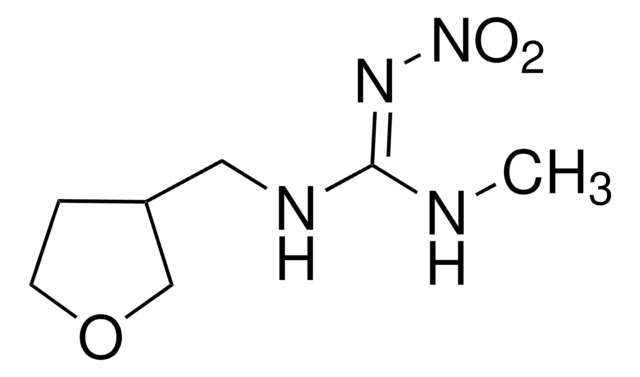
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
analytical standard
Quality Level
product line
PESTANAL®
shelf life
limited shelf life, expiry date on the label
technique(s)
HPLC: suitable
NMR: suitable
gas chromatography (GC): suitable
mp
140-146 °C
suitability
passes test for identity (NMR)
application(s)
agriculture
environmental
format
neat
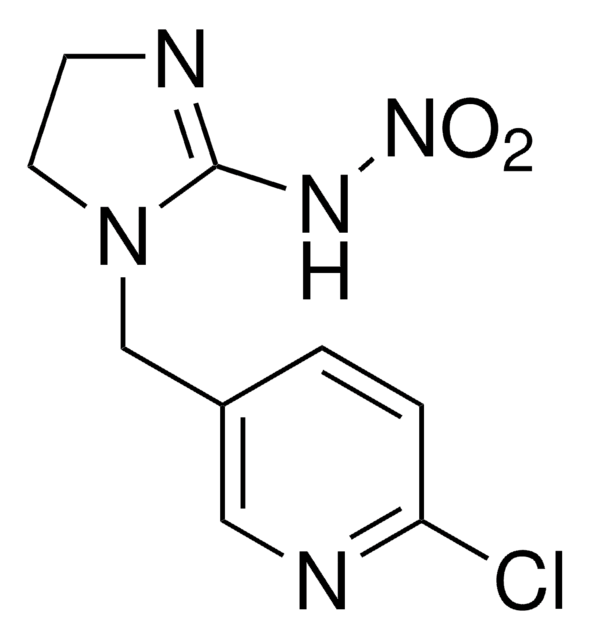
SMILES string
[O-][N+](=O)NC1=NCCN1Cc2ccc(Cl)nc2
InChI
1S/C9H10ClN5O2/c10-8-2-1-7(5-12-8)6-14-4-3-11-9(14)13-15(16)17/h1-2,5H,3-4,6H2,(H,11,13)
InChI key
YWTYJOPNNQFBPC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Find more information here: Neonicotinoids
Application
Legal Information
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1
Storage Class Code
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Determination of Neonicotinoids in Honey using a Chromolith RP-18 HPLC column and UV Detection
Protocols
Honey bee exposure to neonicotinoid pesticides could contribute to colony collapse disorder (CCD). This application utilizes QuEChERS Extraction and LC-MS Analysis.
LC/MS/MS Analysis of Neonicotinoid Pesticides in Dandelion Blossoms on Ascentis® Express C18 after Dispersive SPE (QuEChERS) using Supel™ QuE
Learn more about Neonicotinoids - active substances used in plant protection products to control harmful insects.
On Friday, April 27, 2018, the European Union decided to ban the use of three neonicotinoid insecticides from use on field crops, having deemed them dangerous to bees. This application demonstrates the analysis of these banned compounds and others from dandelion blossoms using QuEChERS and LC-MS.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service