810172P
Avanti
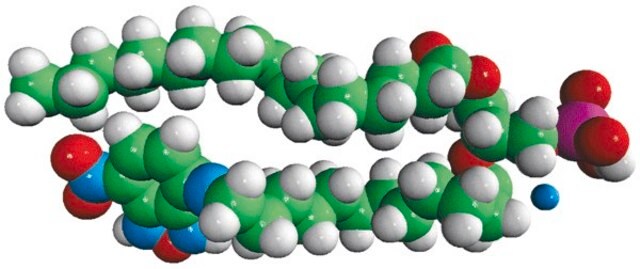
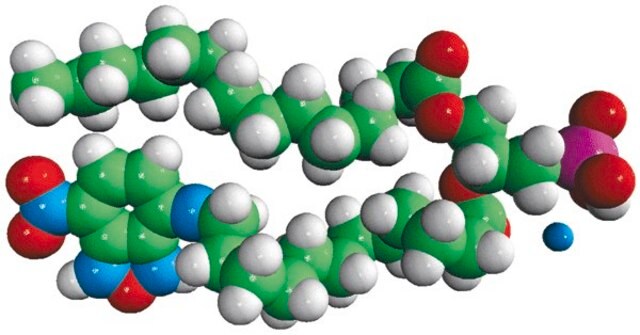
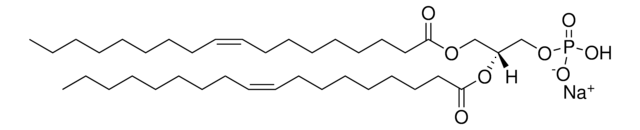
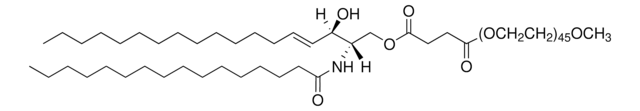
14:0-12:0 NBD PA
Avanti Research™ - A Croda Brand 810172P, powder
Synonym(s):
1-myristoyl-2-{12-[(7-nitro-2-1,3-benzoxadiazol-4-yl)amino]dodecanoyl}-sn-glycero-3-phosphate (ammonium salt)
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C35H62N5O11P
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
759.87
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352211
NACRES:
NA.25
Recommended Products
Assay
>99% (TLC)
form
powder
packaging
pkg of 1 × 1 mg (810172P-1mg)
manufacturer/tradename
Avanti Research™ - A Croda Brand 810172P
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
Phosphatidic acid (PA) is an anionic phospholipid with a phosphomonoester polar head group and two long hydrophobic acyl chains. It constitutes 1-4% of membrane lipids. NBD PA possess fluorescence analog, 7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl (NBD) at sn-2 fatty acid of PA.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Phosphatidic acid (PA) serves as a parent compound to generate other phospholipids. It is a major signaling molecule in the regulation of cellular processes including cell proliferation, secretion and reproduction, cytoskeletal organization, and many more.
Packaging
5 mL Amber Glass Screw Cap Vial (810172P-1mg)
Legal Information
Avanti Research is a trademark of Avanti Polar Lipids, LLC
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documents section.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Phosphatidic acid in membrane rearrangements
Zhukovsky MA, et al.
Febs Letters, 593(17), 2428-2451 (2019)
Mikhail A Zhukovsky et al.
FEBS letters, 593(17), 2428-2451 (2019-08-01)
Phosphatidic acid (PA) is the simplest cellular glycerophospholipid characterized by unique biophysical properties: a small headgroup; negative charge; and a phosphomonoester group. Upon interaction with lysine or arginine, PA charge increases from -1 to -2 and this change stabilizes protein-lipid
A Chauhan et al.
Neurochemical research, 25(3), 423-429 (2000-04-13)
Fibrillar amyloid beta-protein (Abeta) is the major protein of amyloid plaques in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD). The mechanism by which normally produced soluble Abeta gets fibrillized in AD is not clear. We studied the effect of
Karen M Henkels et al.
Oncotarget, 7(30), 47002-47017 (2016-06-04)
The intracellular concentration of the mitogen phosphatidic acid (PA) must be maintained at low levels until the need arises for cell proliferation. How temporal and spatial trafficking of PA affects its target proteins in the different cellular compartments is not
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service