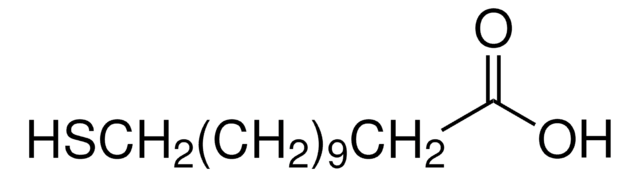448303
16-Mercaptohexadecanoic acid
90%
Synonym(s):
MHDA
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Linear Formula:
HS(CH2)15CO2H
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
288.49
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352103
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
90%
form
solid
mp
65-69 °C
SMILES string
OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCS
InChI
1S/C16H32O2S/c17-16(18)14-12-10-8-6-4-2-1-3-5-7-9-11-13-15-19/h19H,1-15H2,(H,17,18)
InChI key
INOAASCWQMFJQA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
16-Mercaptohexadecanoic acid (MHA) is a long chained alkanethiol which forms self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) on a variety of surfaces.
Application
MHA forms SAMs on gold dipyramids which can be used in the fabrication of nanoresonators for shell-isolated nanoparticle enhanced raman spectroscopy (SHINERS). It can also be used to surface modify gold electrodes that can be used for sensitive detection of clozapine. Gold surfaces can be self-assembled with MHA by polymer pen lithography (PPL) which can be potentially used in bioengineering.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Large-area molecular patterning with polymer pen lithography.
Eichelsdoerfer DJ, et al.
Nature Protocols, 8(12), 2548-2548 (2013)
Landon J Brower et al.
Beilstein journal of nanotechnology, 8, 2307-2314 (2017-11-29)
Integration of surface-anchored metal-organic frameworks (surMOFs) within hierarchical architectures is necessary for potential sensing, electronic, optical, or separation applications. It is important to understand the fundamentals of film formation for these surMOFs in order to develop strategies for their incorporation
Andreas Mark et al.
Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany), 15(43), e1902976-e1902976 (2019-09-24)
The colloidal probe technique, which is based on the atomic force microscope, revolutionizes direct force measurements in many fields, such as interface science or biomechanics. It allows for the first time to determine interaction forces on the single particle or
Brandon H Bowser et al.
Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland), 8(9) (2018-08-26)
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) are extremely porous, crystalline materials with high surface area for potential use in gas storage, sequestration, and separations. Toward incorporation into structures for these applications, this study compares three variations of surface-bound and free-standing HKUST-1 MOF structures:
Sensitive detection of clozapine using a gold electrode modified with 16-mercaptohexadecanoic acid self-assembled monolayer.
Huang Fei, et al.
Talanta, 72(2), 457-462 (2007)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service