201146
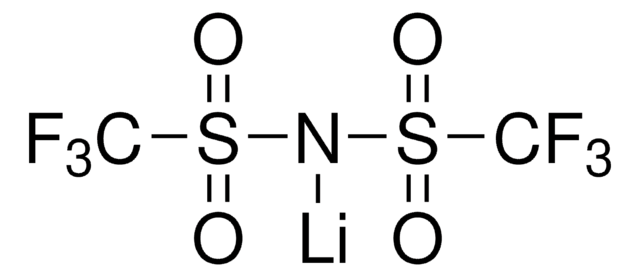
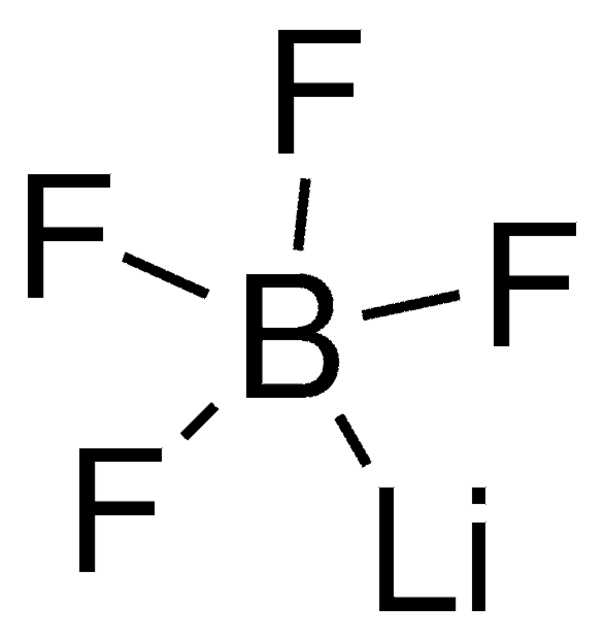
Lithium hexafluorophosphate
98%
Synonym(s):
Lithium phosphorus fluoride
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
for analytical purposes
Assay
98%
form
powder
mp
200 °C (dec.) (lit.)
solubility
H2O: slightly soluble(lit.)
density
1.5 g/mL (lit.)
SMILES string
[Li+].F[P-](F)(F)(F)(F)F
InChI
1S/F6P.Li/c1-7(2,3,4,5)6;/q-1;+1
InChI key
AXPLOJNSKRXQPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
Features and Benefits
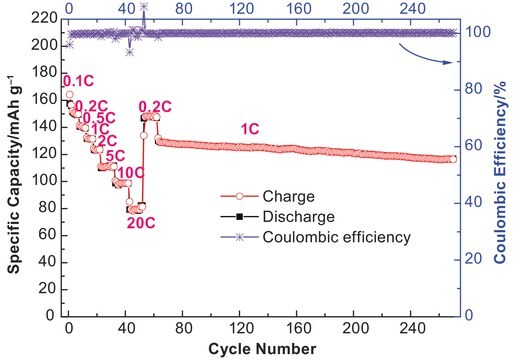
- It can form suitable SEI membranes in electrodes, especially in the cathode
- It can implement passivation for anode current collectors to prevent their dissolution
- Wide windows of electrical stability
- Excellent solubility and high conductivity in various solvents
- Environment-friendly
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1A - STOT RE 1 Inhalation
Target Organs
Bone,Teeth
Storage Class Code
6.1A - Combustible acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Research and development of solid-state lithium fast-ion conductors is crucial because they can be potentially used as solid electrolytes in all-solid-state batteries, which may solve the safety and energy-density related issues of conventional lithium-ion batteries that use liquid (farmable organic) electrolytes.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service