V7259
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor human
≥98% (SDS-PAGE), recombinant, expressed in E. coli, powder, suitable for cell culture
Synonym(s):
VEGF
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor human, VEGF, recombinant, expressed in E. coli, powder, suitable for cell culture
biological source
human
Quality Level
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Assay
≥98% (SDS-PAGE)
form
powder
potency
1-10 ng/mL ED50/EC50
quality
endotoxin tested
mol wt
protein 38.2 kDa (as homodimer)
packaging
pkg of 10 μg
storage condition
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
impurities
≤0.1 EU/μg
color
white
solubility
water: soluble
UniProt accession no.
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
human ... VEGFA(7422)
General description
Application
- the determination of oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs) and luteal cell proliferation/survival
- inducing proliferation of epithelial cell clusters (ECCs) to be transplanted into mice
Biochem/physiol Actions
VEGF recombinant protein might have potential as a therapeutic agent in treatment-resistant disorders, where it can facilitate endothelial cell growth and vessel formation.
Physical properties
Physical form
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
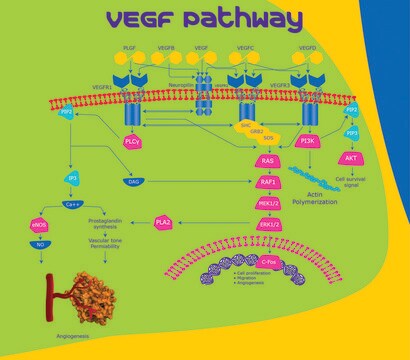
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a family of closely related growth factors having a conserved pattern of eight cysteine residues and sharing common VEGF receptors. VEGF-A (VEGF) is a potent growth factor for blood vessel endothelial cells, showing pleiotropic responses that facilitate cell migration, proliferation, tube formation, and survival. In the developing embryo VEGF-A mRNA is expressed by cells within tissues undergoing capillarization.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service