B3150
Monoclonal Anti-Protein A−Biotin antibody produced in mouse
clone SPA-27, purified immunoglobulin, buffered aqueous solution
Synonym(s):
Monoclonal Anti-Protein A
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
NACRES:
NA.46
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
conjugate
biotin conjugate
antibody form
purified immunoglobulin
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
SPA-27, monoclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
technique(s)
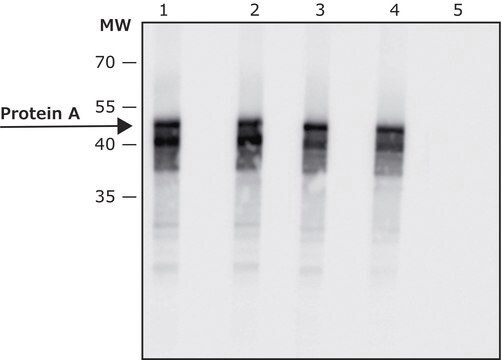
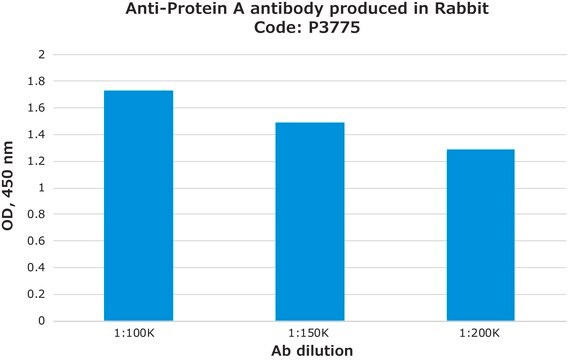
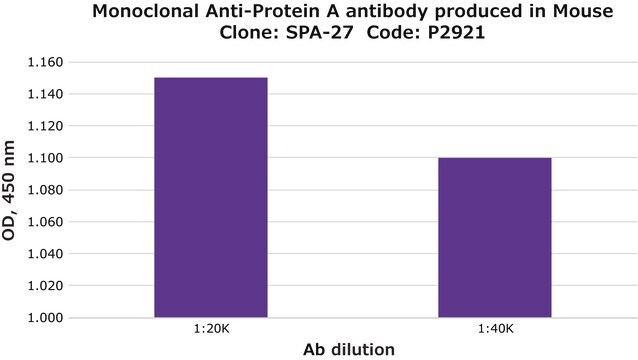
direct ELISA: 1:80,000-1:160,000
isotype
IgG1
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Protein A is a cell wall associated protein isolated from Staphylococcus aureus Cowan 1 strain. The 42 kDa protein consists of a single polypeptide chain. Protein A possesses a specific affinity for Fc region of many mammalian immunoglobulins as human, rabbit, and guinea pig IgGs and therefore, considered as a universal reagent in biochemistry and immunology. Antibodies to protein A have been produced in rabbits, guinea pigs, chickens and mice. Protein A affinity chromatography has been achieved for the purification of immmunoglobulins. Monoclonal Anti-Protein A (mouse IgG1 isotype) is derived from the hybridoma produced by the fusion of mouse myeloma cells and splenocytes from an immunized mouse.
Specificity
Specific for Protein A and shows no cross-reactivity with Protein G. Reacts with free Protein A or IgG bound Protein A and does not interfere with the Fc binding activity of Protein A.
Immunogen
protein A from Cowan I strain of Staphylococcus aureus.
Application
Monoclonal Anti-Protein A-Biotin antibody produced in mouse may be used in ELISA at a working dilution of 1:80,000 - 1:160,000.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Protein A is an immunoglobulin-binding protein present on the surface of Staphylococcus aureus and is also secreted into the extracellular environment. It binds the Fc region of Igs and Fab regions of B cell receptors. The coupling of biotin to monoclonal Anti-Protein A antibody allows for the binding of various labels such as avidin or streptavidin.
Physical form
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 1% inactivated bovine serum albumin and 15 mM sodium azide.
Preparation Note
Prepared by conjugation of biotinamidocaproate N-hydroxysuccinimide ester to fractionated monoclonal anti-Protein A.
Storage and Stability
Store at 2-8 °C for up to one month. For extended storage, solution may be frozen in working aliquots. Repeated freezing and thawing, or storage in "frostfree" freezers, is not recommended. If slight turbidity occurs upon prolonged storage, clarify by centrifugation before use.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
nwg
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Protein A chromatography: challenges and progress in the purification of monoclonal antibodies
Ramos-de-la-Pena AM, et al.
Journal of Separation Science (2019)
Evaluation of indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays and IgG avidity assays using a protein A-peroxidase conjugate for serological distinction between Brucella abortus S19-vaccinated and-infected cows
Pajuaba ACAM, et al.
Clinical and Vaccine Immunology : CVI, 17(4), 588-595 (2010)
Single-domain protein A-engineered magnetic nanoparticles: toward a universal strategy to site-specific labeling of antibodies for targeted detection of tumor cells
Mazzucchelli S, et al.
ACS Nano, 4(10), 5693-5702 (2010)
Antibodies for Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry: Basics and Methods (2009)
Manasi Balachandran et al.
Virulence, 9(1), 390-401 (2017-11-22)
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius is an opportunistic pathogen in dogs and the most frequent cause of canine pyoderma. Protein A, a potent virulence factor in S. aureus is encoded by the spa gene. S. pseudintermedius possesses genes seemingly analogous to spa, but
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service