A1774
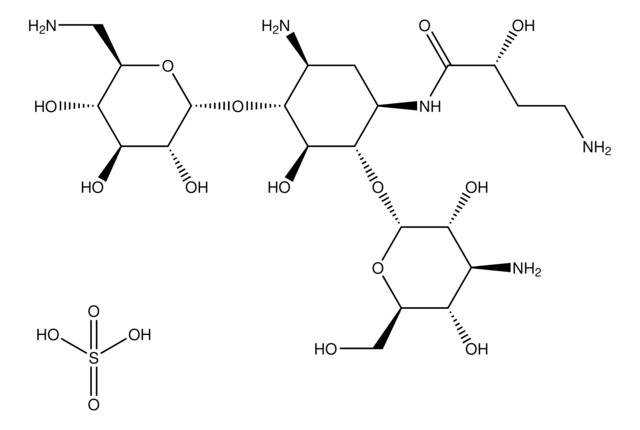
Amikacin disulfate salt
potency: 674-786 μg per mg (as amikacin base)
Synonym(s):
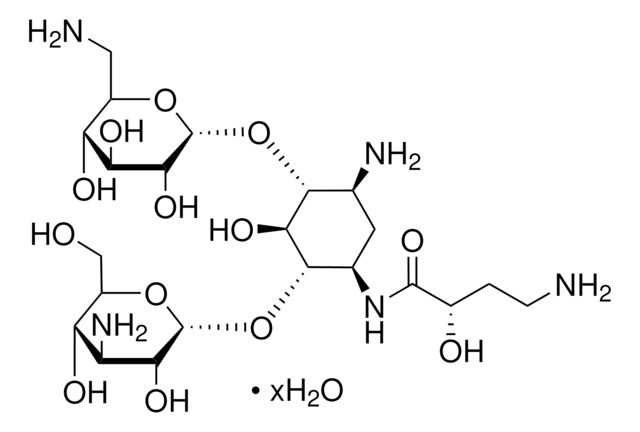
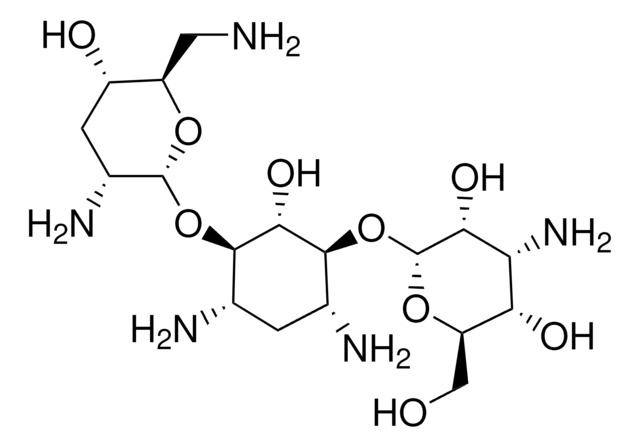
(2S)-4-amino-N-[(1R,2S,3S,4R,5S)-5-amino-2-(3-amino-3-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-4-(6-amino-6-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-3-hydroxycyclohexyl]-2-hydroxybutanamide disulfate, Antibiotic BB-K8 sulfate
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
synthetic
Quality Level
form
powder or crystals
potency
674-786 μg per mg (as amikacin base)
color
white to off-white
antibiotic activity spectrum
Gram-negative bacteria
mycobacteria
Mode of action
protein synthesis | interferes
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
OS(O)(=O)=O.OS(O)(=O)=O.NCC[C@H](O)C(=O)N[C@@H]1C[C@H](N)[C@@H](O[C@H]2O[C@H](CN)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O[C@H]3O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H](N)[C@H]3O
InChI
1S/C22H43N5O13.2H2O4S/c23-2-1-8(29)20(36)27-7-3-6(25)18(39-22-16(34)15(33)13(31)9(4-24)37-22)17(35)19(7)40-21-14(32)11(26)12(30)10(5-28)38-21;2*1-5(2,3)4/h6-19,21-22,28-35H,1-5,23-26H2,(H,27,36);2*(H2,1,2,3,4)/t6-,7+,8-,9+,10+,11-,12+,13+,14+,15-,16+,17-,18+,19-,21+,22+;;/m0../s1
InChI key
FXKSEJFHKVNEFI-GCZBSULCSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Packaging
Other Notes
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Repr. 2 - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service