646547
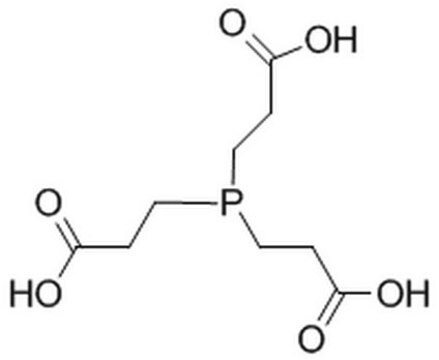
Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine hydrochloride solution
0.5 M, pH 7.0(aqueous solution; pH was adjusted with ammonium hydroxide)
Synonym(s):
TCEP
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
concentration
0.5 M
refractive index
n20/D 1.367
pH
7.0(aqueous solution; pH was adjusted with ammonium hydroxide)
density
1.041 g/mL at 25 °C
SMILES string
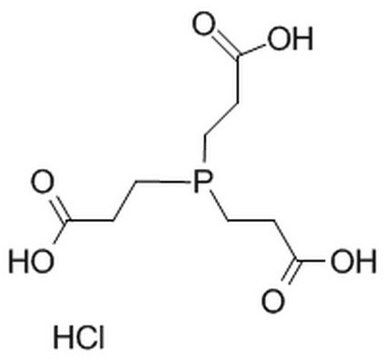
Cl.OC(=O)CCP(CCC(O)=O)CCC(O)=O
InChI
1S/C9H15O6P.ClH/c10-7(11)1-4-16(5-2-8(12)13)6-3-9(14)15;/h1-6H2,(H,10,11)(H,12,13)(H,14,15);1H
InChI key
PBVAJRFEEOIAGW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Related Categories
General description
Application
- to cleave cysteine residues in a synthetic peptide
- in reduction buffer for RNA Sequential Probing of Targets (SPOTs) imaging
- for the reduction of oligonucleotides
- as reducing agent during mitochondrial isolation
Biochem/physiol Actions
accessory
related product
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B
Storage Class Code
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 1
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service


![Tris[(1-benzyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl]amine 97%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/179/695/86a721c8-2a4c-4e4f-bc36-6276ce7a941f/640/86a721c8-2a4c-4e4f-bc36-6276ce7a941f.png)
