M8304
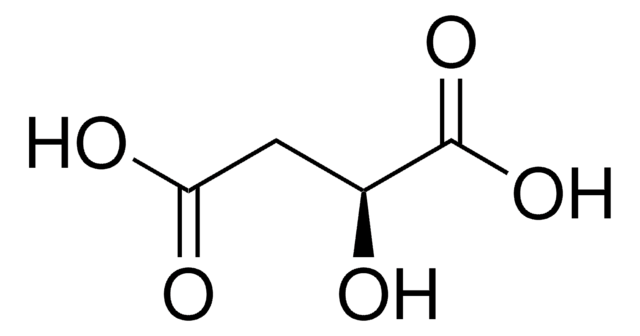
Malic acid
meets USP/NF testing specifications
Synonym(s):
DL-Malic acid, (±)-2-Hydroxysuccinic acid, DL-Hydroxybutanedioic acid
About This Item
Recommended Products
Agency
meets USP/NF testing specifications
Quality Level
vapor density
4.6 (vs air)
vapor pressure
<0.1 mmHg ( 20 °C)
form
solid
autoignition temp.
644 °F
mp
131-133 °C (lit.)
application(s)
pharmaceutical (small molecule)
functional group
carboxylic acid
hydroxyl
SMILES string
OC(CC(O)=O)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C4H6O5/c5-2(4(8)9)1-3(6)7/h2,5H,1H2,(H,6,7)(H,8,9)
InChI key
BJEPYKJPYRNKOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
- Microbiome-metabolomics analysis reveals abatement effects of itaconic acid on odorous compound production in Arbor Acre broilers.: This study explores the role of itaconic acid in reducing odorous compounds in poultry through microbiome and metabolomics analysis (Zhu et al., 2023).
- Influence of Carbon Sources on the Phenolic Compound Production by Euglena gracilis Using an Untargeted Metabolomic Approach.: The research investigates the impact of various carbon sources on phenolic compound production in Euglena gracilis through metabolomics (Bernard and Guéguen, 2022).
- Polymalic acid for translational nanomedicine.: This review highlights the biomedical applications of polymalic acid, focusing on its role in nanomedicine and sustainable production methods (Huang et al., 2022).
- Integrated Proteomics and Metabolomics Analysis of Nitrogen System Regulation on Soybean Plant Nodulation and Nitrogen Fixation.: The study examines the regulatory effects of nitrogen on soybean nodulation and nitrogen fixation using proteomics and metabolomics techniques (Lyu et al., 2022).
- Sustainable production and biomedical application of polymalic acid from renewable biomass and food processing wastes.: This paper discusses the sustainable production of polymalic acid from biomass and its biomedical applications (Zou et al., 2021).
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
397.4 °F
Flash Point(C)
203 °C
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service