A0433
Anti-Albumin antibody produced in rabbit
IgG fraction of antiserum
Synonym(s):
Anti Albumin Antibody
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
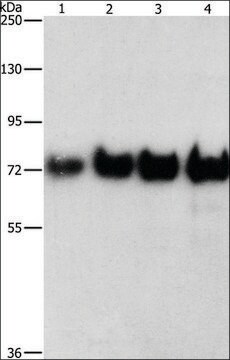
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
IgG fraction of antiserum
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
mol wt
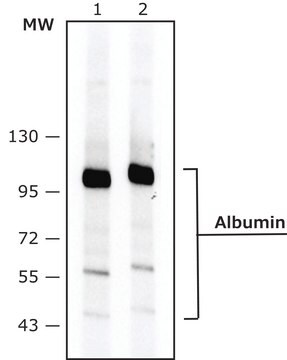
antigen 65 kDa
species reactivity
human
technique(s)
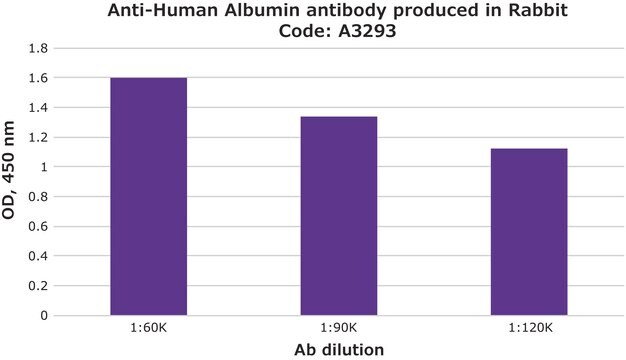
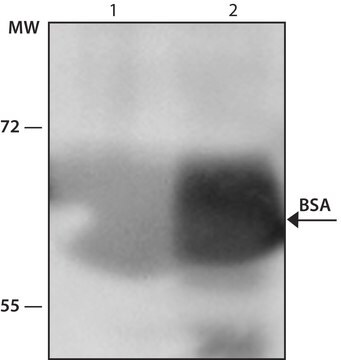
indirect ELISA: 1:25,000
quantitative precipitin assay: 4.0-6.0 mg/mL
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... ALB(213)
General description
Albumin is the most abundant plasma protein in humans.
Albumin, the major protein produced by liver cells, represents more than half of the total protein content of human serum. Many other body fluids also contain albumin.
Specificity
Rabbit polyclonal anti-Albumin antibody reacts with human serum and human albumin.
Immunogen
purified human albumin
Application
Anti-Albumin antibody produced in rabbit has been used in:
- immunocytochemistry
- immunoassay of amino-terminal fragments(ATF)-human serum albumin (HSA)
- canstatin (Can) - human serum albumin (HSA)
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
Biochem/physiol Actions
Three major functions for serum albumin have been proposed: maintenance of osmotic pressure, transportation of a variety of substances and an endogenous source of amino acids. The primary sites of albumin degradation are not known, but the protein can be metabolized by almost every organ in the body. Determination of serum albumin levels is a widely used screening test in clinical medicine. A decrease in serum albumin levels may indicate disease states such as malnutrition, cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome, diabetes, gastrointestinal and hepatic diseases, thermal burns and pulmonary disease. High levels of albumin are associated with dehydration. Albumin turnover is seen in infants with iron deficiency anemia. Advanced liver disease is associated with oxidative damage of albumin.
Physical form
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.2, containing 15 mM sodium azide
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Activin a efficiently specifies definitive endoderm from human embryonic stem cells only when phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling is suppressed
McLean AB, et al.
Stem Cells, 25(1), 29-38 (2007)
Shahid S Siddiqui et al.
American journal of physiology. Lung cellular and molecular physiology, 286(5), L1016-L1026 (2004-01-20)
Vascular endothelial cells undergo albumin endocytosis using a set of albumin binding proteins. This process is important for maintaining cellular homeostasis. We showed by several criteria that the previously described 73-kDa endothelial cell surface albumin binding protein is the 75-kDa
F Apparailly et al.
Gene therapy, 9(3), 192-200 (2002-02-23)
Plasmin is essential for metalloproteases activation, endothelial cell migration and degradation of the extracellular matrix. The process is common to neoangiogenesis pannus formation and cartilage degradation within arthritic joints. Since 80% of synovial cells express urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR)
Siti S Abdullah-Soheimi et al.
Proteome science, 8, 58-58 (2010-11-19)
Diagnosis of ovarian carcinoma is in urgent need for new complementary biomarkers for early stage detection. Proteins that are aberrantly excreted in the urine of cancer patients are excellent biomarker candidates for development of new noninvasive protocol for early diagnosis
Claire Magnon et al.
Cancer research, 65(10), 4353-4361 (2005-05-19)
Canstatin, the noncollagenous domain of collagen type IV alpha-chains, belongs to a series of collagen-derived angiogenic inhibitors. We have elucidated the functional receptors and intracellular signaling induced by canstatin that explain its strong antitumor efficacy in vivo. For this purpose
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service