11296736001
Roche
5-Bromo-2′-deoxy-uridine Labeling and Detection Kit I
sufficient for ≤100 tests, kit of 1 (5 components), suitable for immunofluorescence
Synonym(s):
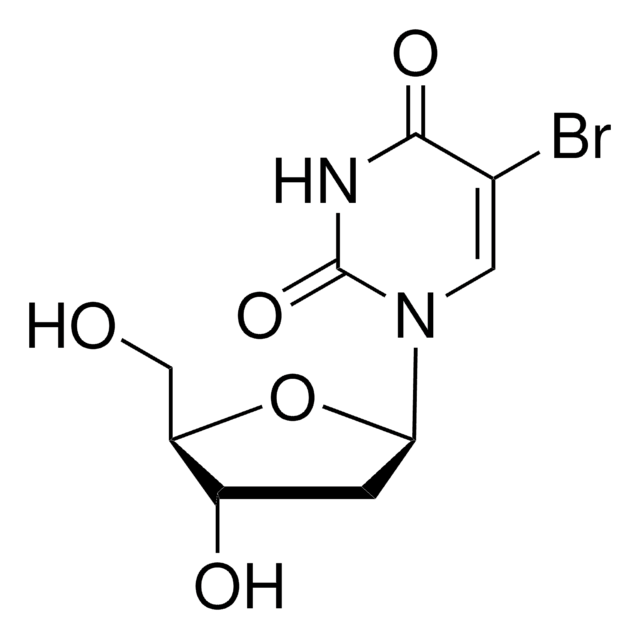
5-BrdU, 5-Bromo-2-deoxyuridine
About This Item
Recommended Products
usage
sufficient for ≤100 tests
Quality Level
packaging
kit of 1 (5 components)
manufacturer/tradename
Roche
technique(s)
immunofluorescence: suitable
storage temp.
−20°C
General description
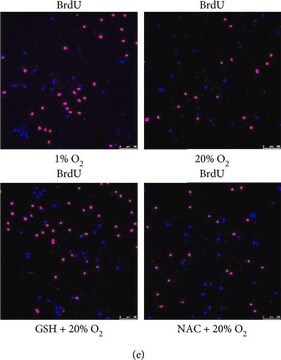
Normally, binding of the antibody is only achieved by denaturation of the DNA. This is usually obtained by exposing the cells to acid, base, or heat. These procedures result in destruction of cell integrity, including cell morphology and surface and cytoplasmatic markers.
The BrdU Labeling and Detection Kit I avoids these problems. The antibody preparation contains specific nucleases which allows access to BrdU after fixation in acidic ethanol. Therefore also simultaneous detection of other markers (double staining) is possible.
Specificity
Application
- Safe: No radioisotopes are used
- Easy to perform: Follows a standard immunofluorescence protocol
- Sensitive: Denaturation of DNA with nucleases allows for highly sensitive detection of BrdU
- Flexible: Allows double-labeling protocols
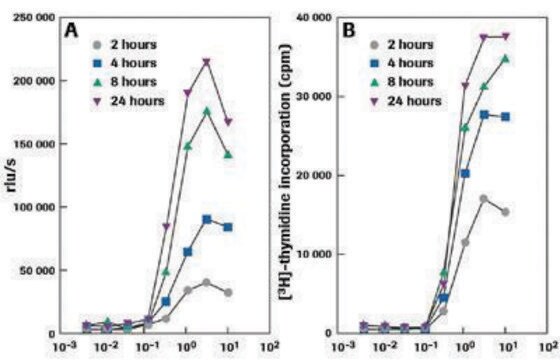
BrdU Labeling and Detection Kit has been used for the detection of 5-bromo-2′-deoxy-uridine (BrdU) incorporated into cellular DNA.
Packaging
Preparation Note
Working solution: BrdU labeling medium
Dilute BrdU labeling reagent 1:1000 with sterile cell culture medium (final concentration 10μM).
Note: For in vivo labeling undiluted BrdU labeling reagent (1 to 2ml/100 g body weight) is needed.
Prepare shortly before use.
Anti-BrdU working solution
Dilute anti-BrdU solution 1:10 with Incubation buffer.
Prepare shortly before use.
Anti-mouse-Ig-fluorescein stock solution
Dissolve anti-mouse-Ig-fluorescein solution in 1ml double-dist. water.
Anti-mouse-Ig-fluorescein working solution
Dilute anti-mouse Ig-fluorescein stock solution 1:10 with PBS. If an extended storage is desired, add BSA (bovine serum albumin), 10 mg/ml.
Prepare shortly before use.
Washing buffer
Dilute Washing buffer concentrate (10x) (bottle 2) 1:10 with double-dist. water.
Storage conditions (working solution): BrdU labeling medium
Store undiluted (1000x) medium in aliquots at -15 to -25°C.
Anti-BrdU working solution
Store undiluted antibody at -15 to -25°C.
Anti-mouse-Ig-fluorescein stock solution
Stable at 2 to 8°C
Washing buffer
Stable at 2 to 8°C
Sample material: Cell culture: adherent cells, suspension cells, organ, or explant cultures. Tissue sections (after in vivo labeling with BrdU).
Other Notes
Kit Components Only
- BrdU Labeling Reagent, sterile 1,000x concentrated
- Washing Buffer concentrate 10x concentrated
- Incubation Buffer
- Anti-BrdU antibody, contains nucleases for DNA denaturation
- Anti-mouse-Ig-fluorescein antibody
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 3 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Muta. 1B - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
does not flash
Flash Point(C)
does not flash
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Cell based assays for cell proliferation (BrdU, MTT, WST1), cell viability and cytotoxicity experiments for applications in cancer, neuroscience and stem cell research.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service