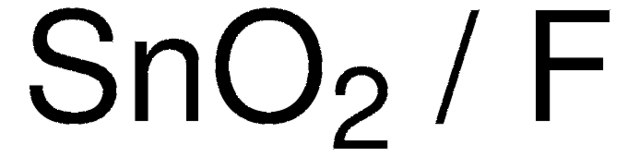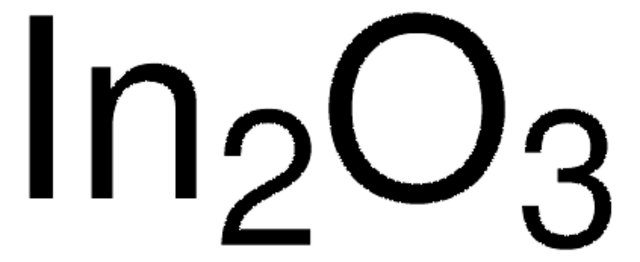703192
Indium tin oxide coated glass slide, square
surface resistivity 8-12 Ω/sq
Synonym(s):
ITO, ITO coated slide, square
About This Item
Recommended Products
description
slide
Quality Level
surface resistivity
8-12 Ω/sq
L × W × thickness
25 mm × 25 mm × 1.1 mm
transmittance
84% (nominal at 550nm)
refractive index
n20/D 1.517
SMILES string
O=[Sn]=O.O=[In]O[In]=O
InChI
1S/2In.5O.Sn
InChI key
LNNWKAUHKIHCKO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
1 of 4
This Item | 327182 | M27301 | 06958 |
|---|---|---|---|
| density 0.894 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) | density 0.875 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) | density 0.956 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) | density 0.899 g/mL at 20 °C, 0.894 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| bp 145 °C (lit.) | bp 61-63 °C/60 mmHg (lit.) | bp 80 °C (lit.) | bp 145 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density >1 (vs air) | vapor density - | vapor density 3 (vs air) | vapor density >1 (vs air) |
| form liquid | form liquid | form liquid | form - |
| refractive index n20/D 1.418 (lit.) | refractive index n20/D 1.410 (lit.) | refractive index n20/D 1.402 (lit.) | refractive index n20/D 1.418 (lit.), n20/D 1.419 |
General description
Application
Physical properties
Storage Class Code
13 - Non Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
In this article, we demonstrate that bis-styrylbenzene derivatives show promising characteristics for very low lasing thresholds and discuss the design considerations for organic lasing molecules.
Professor Shinar (Iowa State University, USA) summarizes the developments of a variety of sensor configurations based on organic and hybrid electronics, as low-cost, disposable, non-invasive, wearable bioelectronics for healthcare.
Organic photovoltaics (OPVs) represent a low-cost, lightweight, and scalable alternative to conventional solar cells. While significant progress has been made in the development of conventional bulk heterojunction cells, new approaches are required to achieve the performance and stability necessary to enable commercially successful OPVs.
Electronically, it behaves as a wide band gap (3.2 eV) semiconductor and exhibits memristor properties.2 Optically, TiO2 has high opacity with a very high refractive index3 (>2.4), and it exhibits strong absorbance in the UV range.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service