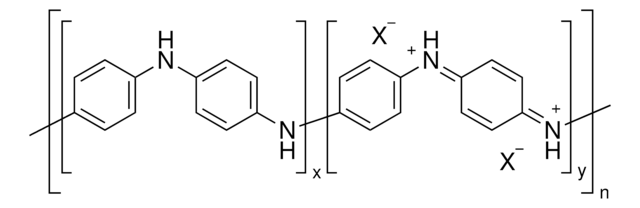
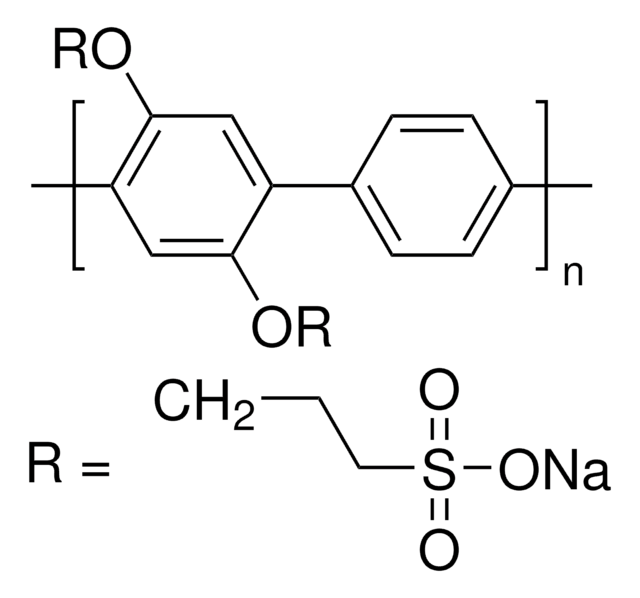
546461
MDMO-PPV
light-emitting polymer
Synonym(s):
Poly[2-methoxy-5-(3′,7′-dimethyloctyloxy)-1,4-phenylenevinylene]
About This Item
Recommended Products
description
Band gap: 2.2 eV
mol wt
Mn ~120,000
solubility
toluene, xylene, THF, chloroform, chlorobenzene, cyclohexanone: soluble
fluorescence
λex 485 nm; λem 555 nm in toluene
Orbital energy
HOMO -5.4 eV
LUMO -3.2 eV
OPV Device Performance
ITO/PEDOT:PSS/MDMO-PPV/PC61BM/Al
ITO/PEDOT:PSS/MDMO-PPV:PC61BM (1:4)/LiF/Al
SMILES string
COc1ccc(OCCC(C)CCCC(C)C)cc1C=C
General description
Application
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
In the emerging field of organic printable electronics, such as OLEDs and organic photovoltaics (OPVs), there is a significant need for improved organic conducting and semiconducting materials. This paper reports our recent progress in two fields: 1) the development of solvent-based dispersions of the intrinsically conducting polymer (ICP) poly(3,4- ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) and 2) the synthesis of new electron-deficient (n-type) semiconducting polymers.
The union of distinct scientific disciplines is revealing the leading edge of Nanotechnology.
The development of high-performance conjugated organic molecules and polymers has received widespread attention in industrial and academic research.
Light-Emitting Polymers
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service![Poly[2-methoxy-5-(2-ethylhexyloxy)-1,4-phenylenevinylene] average Mn 40,000-70,000](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/344/488/b8f8179d-3970-4deb-a754-adda88cdb36f/640/b8f8179d-3970-4deb-a754-adda88cdb36f.png)
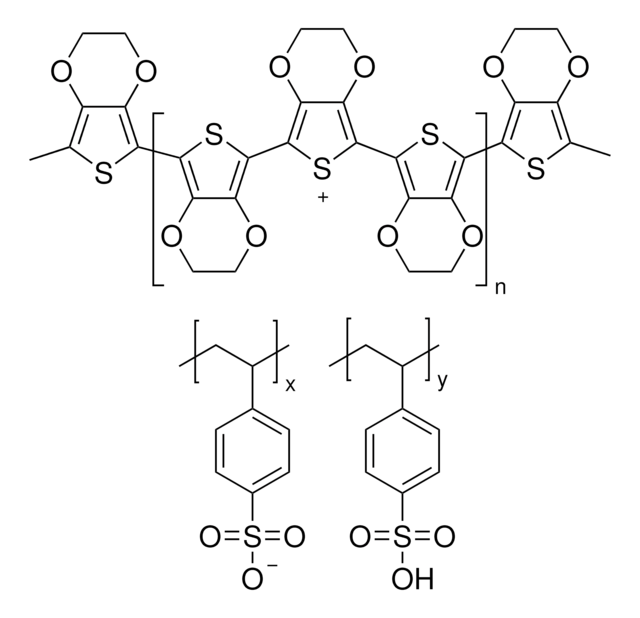

![Poly[5-methoxy-2-(3-sulfopropoxy)-1,4-phenylenevinylene] potassium salt solution 0.25 wt. % in H2O](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/111/584/9e24dfe5-3cb6-4bd8-8bc6-cbe82c1b88cd/640/9e24dfe5-3cb6-4bd8-8bc6-cbe82c1b88cd.png)
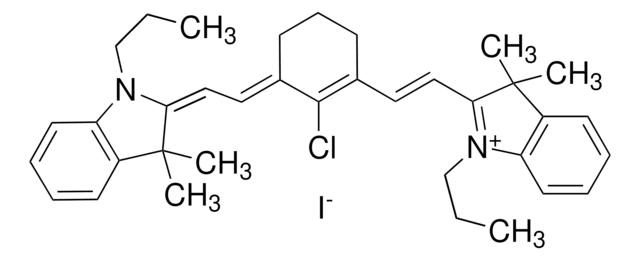

![Poly[(m-phenylenevinylene)-co-(2,5-dioctoxy-p-phenylenevinylene)] light-emitting polymer, predominantly trans](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/249/040/9442b889-4fa0-4b4a-b424-cff0769a5ef2/640/9442b889-4fa0-4b4a-b424-cff0769a5ef2.png)