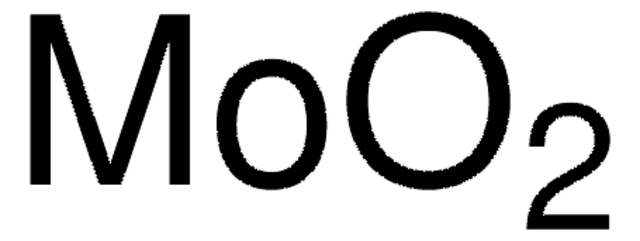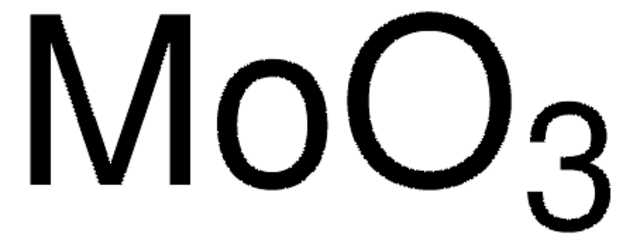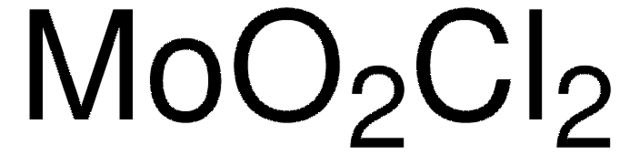203815
Molybdenum(VI) oxide
99.97% trace metals basis
Synonym(s):
Molybdenum trioxide
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
99.97% trace metals basis
form
powder
mp
795 °C (lit.)
application(s)
battery manufacturing
SMILES string
O=[Mo](=O)=O
InChI
1S/Mo.3O
InChI key
JKQOBWVOAYFWKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Carc. 2 - Eye Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Advances in materials have often been led by the development of new synthetic methods that provide control over size, morphology and structure.
Advances in materials have often been led by the development of new synthetic methods that provide control over size, morphology and structure. The preparation of materials in a scalable and continuous manner is critical when development moves beyond lab-scale quantities.
The production of hydrogen by catalytic water splitting is important for a wide range of industries including renewable energy petroleum refining and for the production of methanol and ammonia in the chemical industry.
Professor Chen (Nankai University, China) and his team explain the strategies behind their recent record-breaking organic solar cells, reaching a power conversion efficiency of 17.3%.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service