T6700
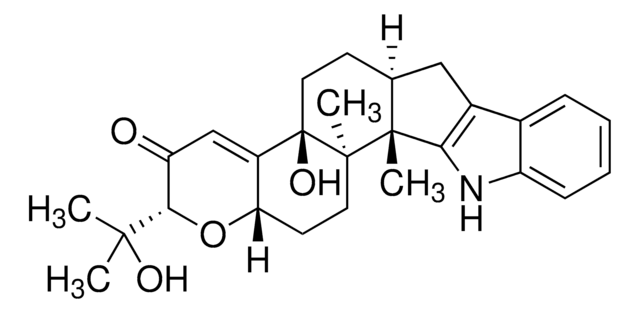
TRAM-34
≥98% (HPLC), solid
Synonym(s):
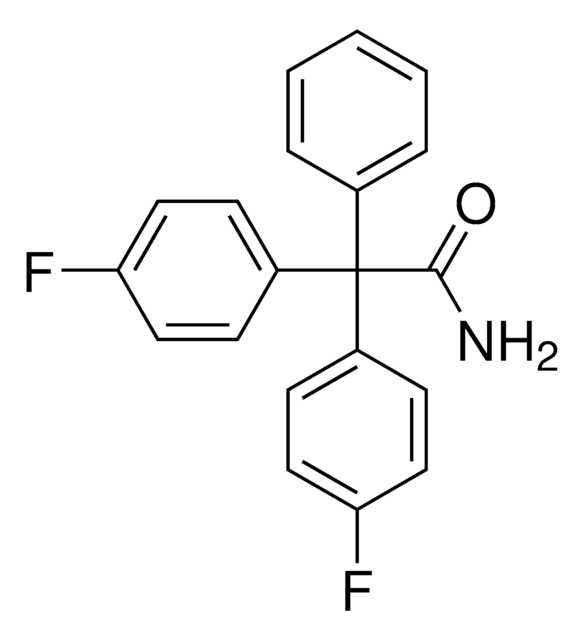
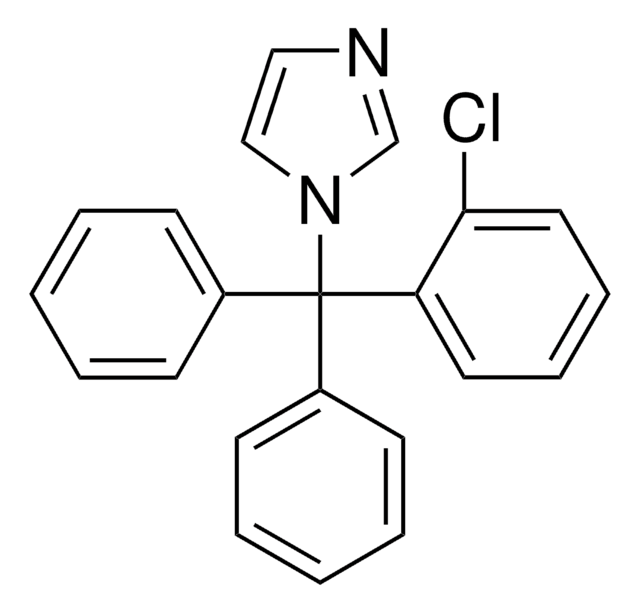
1-[(2-Chlorophenyl)diphenylmethyl]-1H-pyrazole
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C22H17ClN2
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
344.84
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352200
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.77
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
≥98% (HPLC)
form
solid
color
off-white
solubility
DMSO: 2 mg/mL
H2O: insoluble
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
Clc1ccccc1C(c2ccccc2)(c3ccccc3)n4cccn4
InChI
1S/C22H17ClN2/c23-21-15-8-7-14-20(21)22(25-17-9-16-24-25,18-10-3-1-4-11-18)19-12-5-2-6-13-19/h1-17H
InChI key
KBFUQFVFYYBHBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Application
TRAM-34 has been used to study its effect on the prevention of vascular restenosis after balloon angioplasty.
Biochem/physiol Actions
TRAM-34 exhibits 100-fold selectivity (Kd = 20 nM) for IKCa1 channels over other K+ channels (Charybdotoxin, Kd = 5 nM, Clotrimazole, Kd = 70 nM; Nitrendipine Kd = 900 nM). Furthermore, TRAM-34 is known to suppress the activation of human T lymphocytes,.
TRAM-34 is a potent inhibitor of the intermediate-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel.
Features and Benefits
This compound is featured on the Potassium Channels page of the Handbook of Receptor Classification and Signal Transduction. To browse other handbook pages, click here.
Preparation Note
TRAM-34 is soluble in DMSO at 2 mg/ml. However, it is insoluble in water.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 4
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
C Kondo et al.
Experimental physiology, 103(8), 1101-1122 (2018-05-24)
What is the central question of this study? What are the main [Ca2+ ]i signalling pathways activated by ATP in human synovial fibroblasts? What is the main finding and its importance? In human synovial fibroblasts ATP acts through a linked
Nicole Glaser et al.
Pediatric diabetes, 18(5), 356-366 (2016-05-14)
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) causes brain injuries in children ranging from subtle to life-threatening. Previous studies suggest that DKA-related brain injury may involve both stimulation of Na-K-Cl cotransport and microglial activation. Other studies implicate the Na-K-Cl cotransporter and the Ca-activated K
Friederike A Steudel et al.
Molecular oncology, 11(9), 1172-1188 (2017-05-31)
Oncogenic signalling via Ca
Zhihua Yu et al.
Frontiers in cellular neuroscience, 11, 319-319 (2017-10-28)
Ischemic stroke is a devastating neurological disease that can initiate a phenotype switch in astrocytes. Reactive astrogliosis is a significant pathological feature of ischemic stroke and is accompanied by changes in gene expression, hypertrophied processes and proliferation. The intermediate-conductance Ca
Jens G Danielczok et al.
Frontiers in physiology, 8, 979-979 (2017-12-21)
When red blood cells (RBCs) pass constrictions or small capillaries they need to pass apertures falling well below their own cross section size. We used different means of mechanical stimulations (hypoosmotic swelling, local mechanical stimulation, passing through microfluidic constrictions) to
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service