T3038
Trizma® hydrochloride solution
1 M, BioReagent, for molecular biology
Synonym(s):
Tris hydrochloride solution
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
for molecular biology
for molecular biology
Quality Level
sterility
0.2 μm filtered
product line
BioReagent
form
solution
concentration
1 M
impurities
DNase, RNase, NICKase and protease, none detected
pH
8.0
application(s)
agriculture
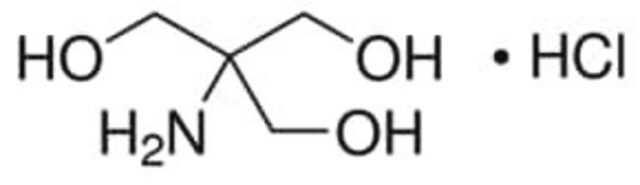
SMILES string
Cl.NC(CO)(CO)CO
InChI
1S/C4H11NO3.ClH/c5-4(1-6,2-7)3-8;/h6-8H,1-3,5H2;1H
InChI key
QKNYBSVHEMOAJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Trizma® hydrochloride solution is a useful biological buffer.
Application
Trizma® hydrochloride solution may be used in the following studies:
- As buffer for the 2-D electrophoresis of rat fibroblast cell.
- As buffer for the rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA (50,000 base pairs or more in length).
- Selective immunoprecipitation of biotin-labeled DNA with antibiotin IgG and Staphylococcus sp.
The pH values of all buffers are temperature and concentration dependent. For Tris buffers, pH increases about 0.03 unit per degree C decrease in temperature, and decreases 0.03-0.05 unit per ten-fold dilution.
For precise applications, use a carefully calibrated pH meter with a glass/calomel combination electrode.
For precise applications, use a carefully calibrated pH meter with a glass/calomel combination electrode.
Other Notes
Prepared with pH-adjusted Biotechnology Performance Certified Trizma Base in 18 megohm water and 0.2 μm filtered.
Legal Information
Trizma is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Lisa W von Friesen et al.
Marine pollution bulletin, 142, 129-134 (2019-06-25)
Standardized methods for the digestion of biota for microplastic analysis are currently lacking. Chemical methods can be effective, but can also cause damage to some polymers. Enzymatic methods are known to be gentler, but often laborious, expensive and time consuming.
P R Langer et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 78(11), 6633-6637 (1981-11-01)
Analogs of dUTP and UTP that contain a biotin molecule covalently bound to the C-5 position of the pyrimidine ring through an allylamine linker arm have been synthesized. These biotin-labeled nucleotides are efficient substrates for a variety of DNA and
M G Murray et al.
Nucleic acids research, 8(19), 4321-4325 (1980-10-10)
A method is presented for the rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA (50,000 base pairs or more in length) which is free of contaminants which interfere with complete digestion by restriction endonucleases. The procedure yields total cellular DNA
Emilie M F Kallenbach et al.
The Science of the total environment, 786, 147455-147455 (2021-05-09)
Chitinaceous organisms have been found to ingest microplastic; however, a standardised, validated, and time- and cost-efficient method for dissolving these organisms without affecting microplastic particles is still required. This study tested four protocols for dissolving organisms with a chitin exoskeleton:
F Gharahdaghi et al.
Electrophoresis, 20(3), 601-605 (1999-04-27)
Mass spectrometry is a powerful technique for the identification of proteins at nanogram quantities. However, some degree of sample preparation prior to mass spectrometry is required, and silver-stained protein gel samples are most problematic. Here we report our strategy to
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service