SRP2123
Sp1 (GC-box binding protein), GST tagged human
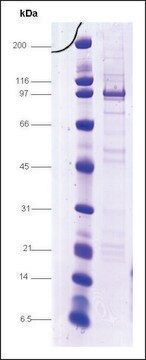
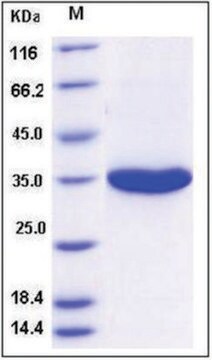
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, ≥70% (SDS-PAGE)
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352202
NACRES:
NA.26
Recommended Products
biological source
human
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Assay
≥70% (SDS-PAGE)
form
frozen liquid
mol wt
~62.8 kDa
packaging
pkg of 10 μg
storage condition
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
concentration
300 μg/mL
color
clear colorless
NCBI accession no.
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−70°C
Gene Information
human ... SP1(6667)
General description
Sp1 is a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein and a eukaryotic transcription factor. It is a ubiquitously expressed nuclear protein. It is one of the first transcription factors to be identified, and the first whose gene was cloned. It was identified as a host factor in HeLa cells, which interacted with the GC-rich sites in SV40 (Simian virus 40) early promoter, and was crucial for in vitro transcription of this promoter. Sp1 is a single polypeptide chain composed of 778 amino acids, and has a molecular weight of 105kDa.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Sp1 binds to GC-rich sequences in a wide variety of promoters. It interacts with cell type or stage-specific transcription factors, and thus, regulates transcription of specific genes. It also controls the formation of the transcription initiation complex. This protein plays a key role in controlling the basal levels of glutathione S-transferase (GSTP1) promoter and the expression of leukotriene C4 synthase gene in the THP-1, a monocyte-like cell line.
Sp1 was first detected in HeLa cells on the basis of its ability to activate the SV40 early promoter transcription. Subsequently it was shown to recognize and bind selectively to a GC-rich consensus sequence (GC-box: GGGCGG or CACCC) that presents in the promoter of several important cellular genes, including SV40 early, HIV-1, PDGF-B etc. Sp1 was the first transcription factor to be cloned and. Analysis of structure and function has revealed that Sp1 can be separated into discrete functional domains. The DNA-binding domain consists of three zinc fingers that specifically bind to the GC-box element. Sp1 contains at least four separate transcriptional activation domains. Two of these domains are glutamine-rich, a well-characterized motif found in several other transcription factors. In addition to transcription, Sp1 function has been linked to cell growth, cancer, Huntington disease and other disorders through transcriptional regulation or specific protein-protein interactions. The function of Sp1 can be regulated by phosphorylation and glycosylation.
Physical form
Clear and colorless frozen liquid solution
Preparation Note
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. While working, please keep sample on ice.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
New insights into the multiple functions of Spl, a ubiquitous transcription factor.
Parnaik VK
Current Science, 76(2), 166-172 (1999)
Sp1 and Sp3 function as key regulators of leukotriene C(4) synthase gene expression in the monocyte-like cell line, THP-1.
Serio KJ et al
American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology, 23(2), 234-240 (2000)
Sp1-mediated transcriptional activation of the human Pi class glutathione S-transferase promoter.
Moffat GJ et al
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271(2), 1054-1060 (1996)
J T Kadonaga et al.
Cell, 51(6), 1079-1090 (1987-12-24)
Transcription factor Sp1 is a protein present in mammalian cells that binds to GC box promoter elements and selectively activates mRNA synthesis from genes that contain functional recognition sites. We have isolated a cDNA that encodes the 696 C-terminal amino
M R Briggs et al.
Science (New York, N.Y.), 234(4772), 47-52 (1986-10-03)
The biochemical analysis of cellular trans-activators involved in promoter recognition provides an important step toward understanding the mechanisms of gene expression in animal cells. The promoter selective transcription factor, Sp1, has been purified from human cells to more than 95
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service