10820
Aprotinin from bovine lung
lyophilized, ~80% (HPCE), crystalline (fine), white, ≥3500 U/mg
Synonym(s):
BPTI, Bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor, Trasylol, Trypsin inhibitor (basic)
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
C284H432N84O79S7
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
6511.44
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352202
NACRES:
NA.26
Recommended Products
biological source
bovine lung
Quality Level
Assay
~80% (HPCE)
form
crystalline (fine)
quality
lyophilized
specific activity
≥3500 U/mg
mol wt
~6,500
technique(s)
electrophoresis: suitable
color
white
solubility
phosphate buffer: 5 mg/mL, clear, colorless (PH 7.6 (70 mm phosphate))
UniProt accession no.
storage temp.
2-8°C
InChI key
ZPNFWUPYTFPOJU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Gene Information
cow ... PTI(404172)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
Aprotinin is largely used as an inhibitor of trypsin.
Biochem/physiol Actions
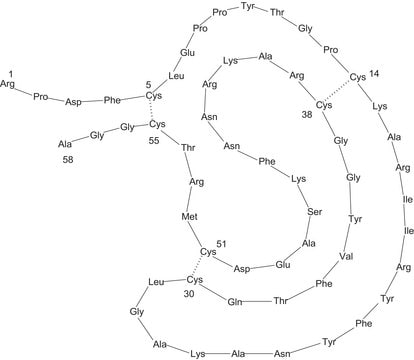
Aprotinin is a competitive serine protease inhibitor that forms stable complexes with and blocks the active sites of enzyme. This binding is reversible, and most aprotinin-protease complexes will dissociate at extreme pH levels >10 or <3. Structurally, Aprotinin is a monomeric globular protein derived from bovine lung that consists of 58 amino acids, arranged in a single polypeptide chain with three crosslinking disulfide bridges.
Unit Definition
1 U corresponds to 1 biological kallikrein inhibitor unit (KIU)
One Trypsin Inhibitor Unit (TIU) will decrease the activity of two trypsin units by 50%, where one trypsin unit will hydrolyze 1.0 μmole of N-alpha-benzoyl-DL-arginine p-nitroanilide per minute at pH 7.8 and 25°C. Another commonly used unit is the KIU, with 1 TIU = 1,300 KIU.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Susan E Logue et al.
Nature protocols, 4(9), 1383-1395 (2009-09-05)
Apoptosis is a mode of programmed cell death that is widely used to eliminate cells during development, tissue homeostasis, infection or in response to injury. Alterations to the plasma membranes of apoptotic cells trigger recognition and engulfment of such cells
Axel Himmelbach et al.
Bio-protocol, 8(15), e2955-e2955 (2018-08-05)
Chromosome conformation capture sequencing (Hi-C) is a powerful method to comprehensively interrogate the three-dimensional positioning of chromatin in the nucleus. The development of Hi-C can be traced back to successive increases in the resolution and throughput of chromosome conformation capture
Hamid Ebrahimi Orimi et al.
Scientific reports, 10(1), 9730-9730 (2020-06-18)
We introduced and validated a drop-on-demand method to print cells. The method uses low energy nanosecond laser (wavelength: 532 nm) pulses to generate a transient microbubble at the distal end of a glass microcapillary supplied with bio-ink. Microbubble expansion results in
Roberta De Tullio et al.
Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.), 1915, 163-185 (2019-01-09)
The production of recombinant calpastatin in E. coli has become an efficient tool to obtain discrete amounts of a specific calpastatin species that can be present concomitantly with other calpastatin fragments/forms in the same tissue or cell type in a
Robert E G Riddell et al.
Canadian journal of anaesthesia = Journal canadien d'anesthesie, 60(1), 16-23 (2012-11-08)
In light of the concerns about the safety of aprotinin, we wanted to determine if aprotinin use during cardiac surgery was associated with an increased risk of mortality and morbidity compared with the use of tranexamic acid (TXA). We hypothesized
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service