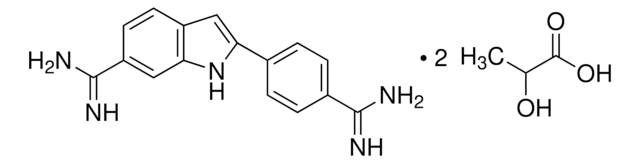
Recommended Products
General description
DAPI: 4′, 6-Diamino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride. Antifade Solution: p-Phenylenediamine and glycerol in PBS solution. 0.4μg/mL DAPI suspended in Antifade. The product is ready to add to fixed slides or cells cultures.
Application
A nuclear fluorescent stain used for counterstaining paraffin-embedded, formalin-fixed tissue, metaphase chromosomes, or interphase nuclei that have been hybridized with probes detected with Fluorescein, or equivalent stains. Antifade prevents the permanent loss of fluorescence or fluorescent signal quenching due to photobleaching and prolonged exposure to high intensity light sources.
DAPI binds the minor groove of DNA at AT clusters and binds preferentially to ds DNA (Biochemistry 26:4545, 1987).
Materials Provided
Each vial contains 1 ml of DAPI/Antifade Solution
Warnings and Precautions
DAPI is a potential carcinogen. Antifade is a potential toxin and irritant. Use extreme caution. Avoid contact with eyes, skin and mucous membranes. Use extreme caution. Wear gloves and a lab coat when handling. Follow your institution′s guidelines for hazardous waste disposal. Keep tightly capped and limit exposure to light.
Related Products
Antifade Solution S7114
Propidium Iodide Solution S7109
Propidium Iodide/Antifade Solution S7112
DAPI binds the minor groove of DNA at AT clusters and binds preferentially to ds DNA (Biochemistry 26:4545, 1987).
Materials Provided
Each vial contains 1 ml of DAPI/Antifade Solution
Warnings and Precautions
DAPI is a potential carcinogen. Antifade is a potential toxin and irritant. Use extreme caution. Avoid contact with eyes, skin and mucous membranes. Use extreme caution. Wear gloves and a lab coat when handling. Follow your institution′s guidelines for hazardous waste disposal. Keep tightly capped and limit exposure to light.
Related Products
Antifade Solution S7114
Propidium Iodide Solution S7109
Propidium Iodide/Antifade Solution S7112
Physical form
Liquid PBS pH 8.0 containing ~50% glycerol and 0.4μg/mL of DAPI and 2-7mM phenylenediamine.
Storage and Stability
Store at -20ºC in undiluted aliquots for up to 1 year from date of receipt. Protect from light
Legal Information
CHEMICON is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 3
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Effects of RGDS sequence genetically interfused in the silk fibroin light chain protein on chondrocyte adhesion and cartilage synthesis.
Yusuke Kambe,Koji Yamamoto,Katsura Kojima,Yasushi Tamada,Naohide Tomita
Biomaterials null
Creation of Biofunctionalized Micropatterns on Poly(methyl methacrylate) by Single-Step Phase Separation Method.
Ho QP, Wang SL, Wang MJ
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces null
Observation of chondrocyte aggregate formation and internal structure on micropatterned fibroin-coated surface.
Naoyoshi D Kachi,Akihisa Otaka,Seungwoo Sim,Yoshihiko Kuwana,Yasushi Tamada,Junko Sunaga et al.
Bio-medical materials and engineering null
Mohammadhossein Khorraminejad-Shirazi et al.
Stem cell research & therapy, 11(1), 45-45 (2020-02-06)
Mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC) stemness capacity diminishes over prolonged in vitro culture, which negatively affects their application in regenerative medicine. To slow down the senescence of MSCs, here, we have evaluated the in vitro effects of 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR), an
Kuan-Jung Chen et al.
Journal of cell science, 133(3) (2020-01-15)
Cell migration requires the coordination of multiple signaling pathways involved in membrane dynamics and cytoskeletal rearrangement. The Arf-like small GTPase Arl4A has been shown to modulate actin cytoskeleton remodeling. However, evidence of the function of Arl4A in cell migration is
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service