740713
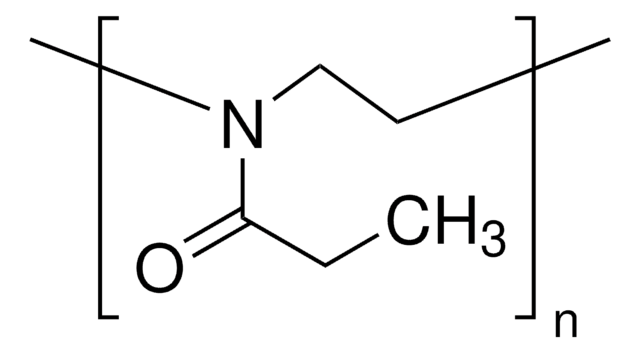
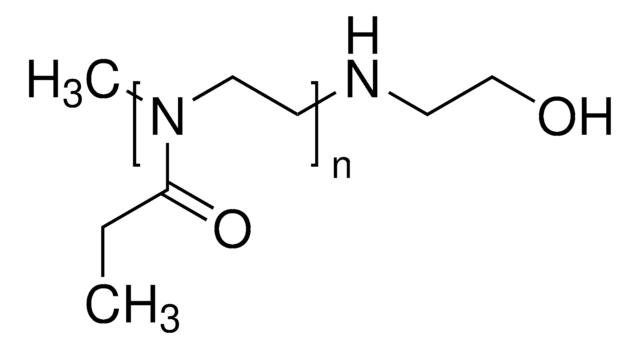
Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)
average Mn 5,000, PDI ≤1.3
Synonym(s):
PEOX Polymer
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
solid
mol wt
average Mn 5,000
PDI
≤1.3
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
- Two-photon polymerized poly (2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) hydrogel 3D microstructures: This study presents a novel hydrogel platform based on poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) that allows for the creation of 3D microstructures with tunable mechanical properties, suitable for tissue engineering applications (Czich et al., 2020).
- High definition fibrous poly (2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) scaffolds: This research explores the use of melt electrospinning writing to create high-definition scaffolds from poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline), highlighting its potential for creating precise and customizable structures in biomedical applications (Hochleitner et al., 2014).
- Synthesis and evaluation of methacrylated poly (2-ethyl-2-oxazoline): This study focuses on the synthesis of methacrylated poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) for use as a mucoadhesive polymer, demonstrating its potential in enhancing nasal drug delivery systems (Shan et al., 2021).
- High-definition poly (2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) scaffolds: Investigates the use of melt electrospinning writing to fabricate scaffolds from poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline), a polymer that offers promise due to its high melting temperature and hydrophilic nature, suitable for various biomedical applications (Hochleitner et al., 2014).
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
Poly(2-oxazoline)s (POx) can be viewed as conformational isomers of polypeptides. They are synthesized via living cationic ringopening polymerization (LCROP) of 2-oxazolines and were almost simultaneously discovered in 1966 by the groups of Litt, Tomalia, Fukui and Seeliger.
The introduction of polymers into the biomedical field has opened new avenues in tissue engineering, implant design, biosensing, and drug delivery.
Wide range of functional polymers for biomedical applications have been synthesized and structurally characterized. Several classes of polymers including biodegradable polymers, hydrophilic & amphiphilic polymers, and stimuli responsive polymers have been prepared using controlled and directed functionalization via "living" polymerization such as RAFT, ionic and ring opening polymerization. Selected polymers have been studied for their structure-properties relationship. "
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service