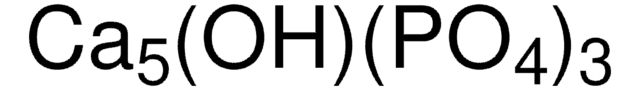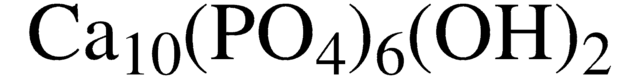702153
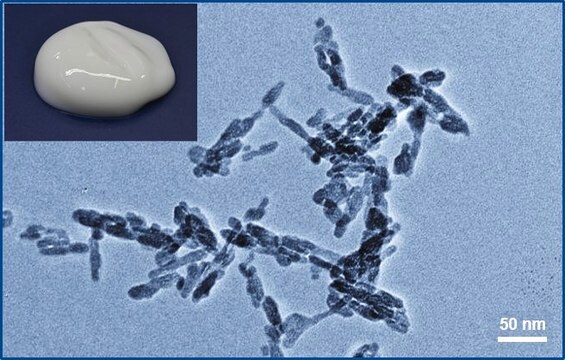
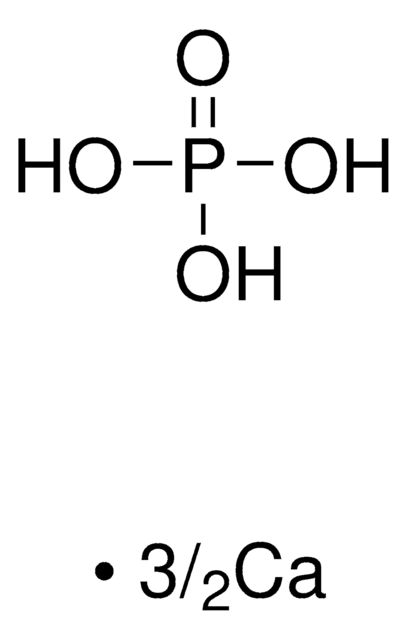
Hydroxyapatite
nanoparticles, dispersion, 10 wt. % in H2O, <200 nm particle size (BET)
Synonym(s):
Calcium hydroxide phosphate, Calcium hydroxylapatite, Calcium hydroxyphosphate, Nano hydroxyapatatite, Pentacalcium hydroxide triphosphate
About This Item
nanoparticles
Recommended Products
grade
for analytical purposes
Quality Level
form
dispersion
nanoparticles
contains
≤0.025 wt. % dispersant (non-metal based)
concentration
10 wt. % in H2O
surface area
14.3 m2/g , typical
particle size
<200 nm (BET)
pH
4-6
density
1.038 g/mL at 25 °C
SMILES string
[Ca++].[Ca++].[Ca++].[Ca++].O[Ca+].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O
InChI
1S/5Ca.3H3O4P.H2O/c;;;;;3*1-5(2,3)4;/h;;;;;3*(H3,1,2,3,4);1H2/q5*+2;;;;/p-10
InChI key
XYJRXVWERLGGKC-UHFFFAOYSA-D
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Application
- An implant material for bone substitute due to its chemical similarity to the inorganic component of bone and osteo inductive properties.
- A vehicle for gene and drug delivery because of its encapsulation capacity and affinity to several drugs and proteins.
- A pH responsive particulate emulsifier.
Features and Benefits
- Biocompatible
- Osteoconductive
- Stable under physiological conditions
- High mechanical strength
Legal Information
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications
A key challenge for nanomaterial safety assessment is the ability to handle the large number of newly engineered nanomaterials (ENMs), including developing cost-effective methods that can be used for hazard screening.
Global Trade Item Number
| SKU | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 702153-25ML | 4061832820743 |
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service