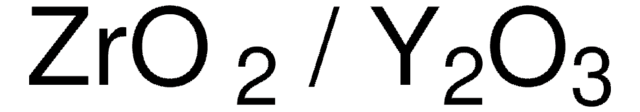544779
Zirconium(IV) oxide-yttria stabilized
<100 nm particle size
Synonym(s):
YSZ-3, YSZ-8, YSZ, Yttria stabilized zirconia, Yttrium stabilized zirconium oxide
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
(ZrO2)1-x(Y2O3)x
UNSPSC Code:
26111700
NACRES:
NA.23
Recommended Products
form
powder
contains
8% yttria as stabilizer
composition
(ZrO2)1-x(Y2O3)x
greener alternative product characteristics
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
surface area
<60 m2/g , BET
particle size
<100 nm
greener alternative category
Related Categories
General description
We are committed to bringing you Greener Alternative Products, which adhere to one or more of The 12 Principles of Greener Chemistry. This product has been enhanced for energy efficiency. Click here for more details.
Yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) is the most commonly used solid electrolyte for solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) and oxygen sensors. YSZ exhibits high oxygen-ionic conductivity while blocking electronic conduction. YSZ particles may be synthesized from yttrium nitrate or isopropoxide by sol gel method. YSZ nanoparticles may be prepared in supercritical water (SCW). YSZ nanoparticles of different sizes with varying % mol of yttria may be obtained by CO2 laser based continuous/pulsed laser vaporization method.
Zirconium(IV) oxide-yttria stabilized (YSZ) (<100 nm particle size) is an oxygen ion conductor with properties such as good ionic conductivity and high physiochemical stability. Its other properties include excellent shock resistance, low thermal conductivity and a high coefficient of thermal expansion.
Application
Collagen-yttria-stabilized amorphous zirconia hybrid scaffolds may be developed. YSZ thin films may be used as thermal barrier coatings on combustors, stationary and rotating components of gas turbines or diesel engines. 6
YSZ can be used for a variety of applications such as:
- a thermal barrier coating for the protection and insulation of metal components in gas turbines
- an electrolyte in the fabrication of solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs)
- in the fabrication of zirconia dental implant abutments
- membranes for micro energy conversion devices
- a solid acid and a catalyst for catalytic applications
Packaging
Packaged in glass bottles
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Zigzag or spiral-shaped nanostructures improve mechanical stability in yttria-stabilized zirconia membranes for micro-energy conversion devices
Shi Y, et al.
Nano Energy, 59(1), 674-682 (2019)
Fracture resistance of yttria-stabilized zirconia dental implant abutments
Adatia ND, et al.
Journal of Prosthodontics : Official Journal of the American College of Prosthodontists, 18(1), 17-22 (2009)
Confined Transformation of UiO-66 Nanocrystals to Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia with Hierarchical Pore Structures for Catalytic Applications
Qin R and Zeng H
Advances in Functional Materials, 29(39), 1903264-1903264 (2019)
Thermodynamic vaporization studies of the manganese oxide--yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) solid solution
Matraszek A, et al.
J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 24(9), 2649-2656 (2004)
Impedance spectroscopy of pellets made from yttria stabilized zirconia nanoparticles generated via CW and pulsed mode of laser vaporization method
Khare J, et al.
Ceramics International, 40(9) Part B, 14677-14685 (2014)
Articles
Advances in Materials for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service