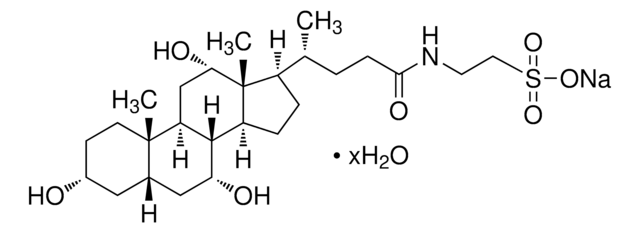
T4009
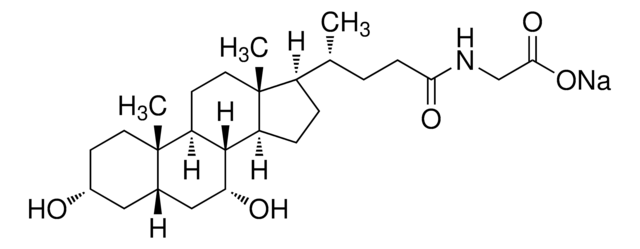
Acide taurocholique sodium salt hydrate
≥95% (HPLC)
Synonyme(s) :
N-(2-sulfoéthyl)amide de l’acide 3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oïque, Acide 2-[(3α,7α,12α-trihydroxy-24-oxo-5β-cholan-24-yl)amino]éthanesulfonique, Taurocholate de sodium hydrate
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
synthetic (organic)
Niveau de qualité
Description
anionic
Essai
≥95% (HPLC)
Forme
powder
Poids mol.
micellar avg mol wt 2100
Nombre d'agrégation
4
CMC
3-11 mM (20-25°C)
Groupe fonctionnel
sulfonic acid
Conditions d'expédition
ambient
Température de stockage
room temp
Chaîne SMILES
[Na+].[H]O[H].[H][C@@]12C[C@H](O)CC[C@]1(C)[C@@]3([H])C[C@H](O)[C@]4(C)[C@H](CC[C@@]4([H])[C@]3([H])[C@H](O)C2)[C@H](C)CCC(=O)NCCS([O-])(=O)=O
InChI
1S/C26H45NO7S.Na.H2O/c1-15(4-7-23(31)27-10-11-35(32,33)34)18-5-6-19-24-20(14-22(30)26(18,19)3)25(2)9-8-17(28)12-16(25)13-21(24)29;;/h15-22,24,28-30H,4-14H2,1-3H3,(H,27,31)(H,32,33,34);;1H2/q;+1;/p-1/t15-,16+,17-,18-,19+,20+,21-,22+,24+,25+,26-;;/m1../s1
Clé InChI
RDAJAQDLEFHVNR-NEMAEHQESA-M
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Notes préparatoires
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Isobaric separation of bile acids and conjugates by LC-MS/MS on Ascentis® Express C18 column with excellent resolution and linearity.
The liver excretes excess cholesterol in the form of bile acids. Bile acids serve two purposes: to remove unwanted cholesterol from the body and to aid in lipid digestion in the intestine.
Today, diverse studies report the benefits of probiotics, such as inhibitory effects on pathogens, aid in the management or prevention of chronic intestinal inflammatory diseases or atopic syndromes, and support to the immune system. Potential beneficial applications abound, researchers continue to evaluate the effictiveness and clarify the mechanisms of action of probiotics.
Protocoles
This method is particularly useful in research into the role of individual bile acids as signaling molecules; suitable for clinical laboratories to investigate potential mechanisms linked to gut hormone profiles and glycemic control.
Contenu apparenté
Bile Acids (BA) are synthesized in the liver and play important roles in cholesterol homeostasis, absorption of vitamins and lipids, and various key metabolic processes.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique