T3038
Trizma® hydrochloride solution
1 M, BioReagent, for molecular biology
Synonyme(s) :
Tris hydrochloride solution
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Qualité
for molecular biology
for molecular biology
Niveau de qualité
Stérilité
0.2 μm filtered
Gamme de produits
BioReagent
Forme
solution
Concentration
1 M
Impuretés
DNase, RNase, NICKase and protease, none detected
pH
8.0
Application(s)
agriculture
Chaîne SMILES
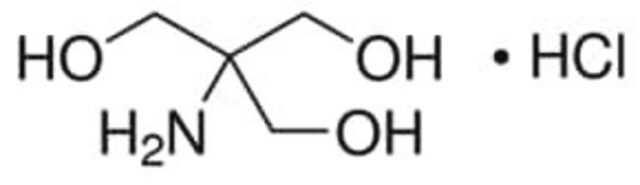
Cl.NC(CO)(CO)CO
InChI
1S/C4H11NO3.ClH/c5-4(1-6,2-7)3-8;/h6-8H,1-3,5H2;1H
Clé InChI
QKNYBSVHEMOAJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
- As buffer for the 2-D electrophoresis of rat fibroblast cell.
- As buffer for the rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA (50,000 base pairs or more in length).
- Selective immunoprecipitation of biotin-labeled DNA with antibiotin IgG and Staphylococcus sp.
For precise applications, use a carefully calibrated pH meter with a glass/calomel combination electrode.
Autres remarques
Informations légales
Code de la classe de stockage
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique