S7820
α-Synuclein human
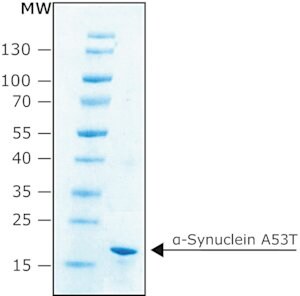
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, N-terminal histidine tagged, ≥90% (SDS-PAGE), lyophilized powder
Synonyme(s) :
α-Synuclein protein, Synuclein protein
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Produit recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Niveau de qualité
Essai
≥90% (SDS-PAGE)
Forme
lyophilized powder
Numéro d'accès UniProt
Conditions d'expédition
dry ice
Température de stockage
−20°C
Informations sur le gène
human ... SNCA(6622)
Description générale
α-Synuclein is an intrinsically disordered protein predominantly expressed in the dopaminergic neurons. It is localized to the presynaptic nerve terminals and is highly conserved in vertebrates.
Application
α-Synuclein human has been used to study the α-syn monomers and its aggregates on paraformaldehyde (PFA)-fixed membrane. It has also been used to study its effect on neurotransmitter levels (monoamines and amino acid concentration) tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and transglutaminase-2 (TG2) mRNA expression in the mouse striata (ST).
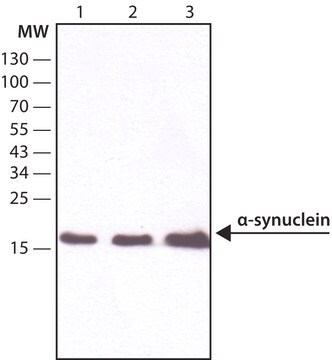
Human α-synuclein has been used to study the immunodetection of α-syn monomers and its aggregates. It has also been used in microscale thermophoresis to study protein-protein interactions.
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
140-amino acid protein (apparent molecular weight 19-20 kDa) encoded by a simple gene consisting of six exons on human chromosome 4. Induces polymerization of tubulin into microtubules and functions in the modulation of dopamine transporter function, regulating the synaptic tone of dopamine. Disruption of this function can ultimately lead to neurodegeneration of nerve terminals. Highly abundant in presynaptic terminals, a major component of Lewy bodies, the neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions that are a hallmark of diverse neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson′s disease (PD), dementia with Lewy bodies (filamentous inclusions), Lewy body variant of Alzheimer′s disease, and multiple system atrophy. Pathogenic point mutations in the α-synuclein gene are linked to familial Parkinson′s disease.
140-amino acid protein (apparent molecular weight 19-20 kDa) that induces polymerization of tubulin into microtubules and functions in the modulation of dopamine.
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Prolyl Oligopeptidase Enhances a-Synuclein Dimerization via Direct Protein-Protein Interaction*
Mari H. Savolainen
The Journal of Biological Chemistry (2015)
Residual structure, backbone dynamics, and interactions within the synuclein family
Sung YH and Eliezer D
Journal of Molecular Biology, 372(3), 689-689 (2007)
Juan A Gerez et al.
Science translational medicine, 11(495) (2019-06-07)
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by the progressive accumulation of neuronal α-synuclein (αSyn) inclusions called Lewy bodies. It is believed that Lewy bodies spread throughout the nervous system due to the cell-to-cell propagation of αSyn via cycles
Effects of alpha-Synuclein Monomers Administration in the Gigantocellular Reticular Nucleus on Neurotransmission in Mouse Model
Joniec MI, et al.
Neurochemical Research, 44(4), 968-977 (2019)
Improved Immunodetection of Endogenous a-Synuclein
Byung Rho Lee
PLoS ONE (2011)
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique