P0122
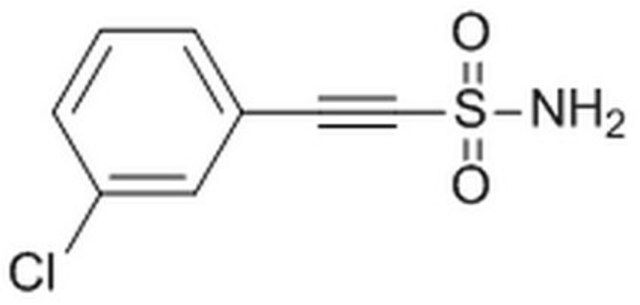
Pifithrin-μ
≥97% (HPLC), solid
Synonyme(s) :
2-Phenyl-ethynesulfoanide, PFT-μ
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Essai
≥97% (HPLC)
Forme
solid
Conditions de stockage
desiccated
Solubilité
DMSO: soluble >10 mg/mL, clear
H2O: insoluble
Température de stockage
2-8°C
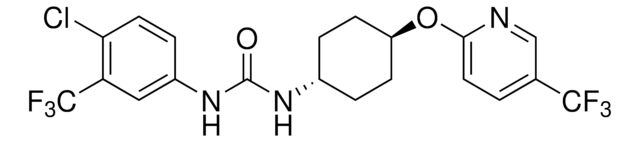
Chaîne SMILES
NS(=O)(=O)C#Cc1ccccc1
InChI
1S/C8H7NO2S/c9-12(10,11)7-6-8-4-2-1-3-5-8/h1-5H,(H2,9,10,11)
Clé InChI
ZZUZYEMRHCMVTB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Application
- to treat microglial cell line to analyse its neuroprotective effect on M1-like and M2-like phenotype
- as heat shock protein (HSP)-70 inhibitor, to treat transfected Marc-145 cells
- to inhibit heat shock cognate 70 (Hsc70) to elucidate heat shock chaperones mouse embryonic stem cells
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 4 Oral
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique