F0427
Fas Ligand human
>95% (SDS-PAGE), recombinant, expressed in CHO cells, lyophilized powder
Synonyme(s) :
FasL
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Produit recombinant
expressed in CHO cells
Niveau de qualité
Essai
>95% (SDS-PAGE)
Forme
lyophilized powder
Poids mol.
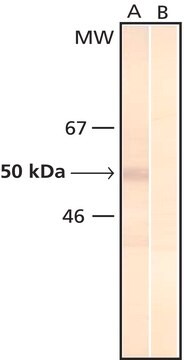
monomer calculated mol wt ~18 kDa
26-28 kDa by SDS-PAGE
Impuretés
endotoxin, tested
Numéro d'accès UniProt
Température de stockage
−20°C
Informations sur le gène
human ... FASLG(356)
Catégories apparentées
Description générale
FASLG (Fas ligand) acts as a ligand for Fas receptor, and is a major protein involved in programmed cell death, apoptosis. Soluble Fas (sFAS) is usually detected in plasma prior to apoptosis.
Application
Fas Ligand (FASLG) human has been used for-
- the study of FASLG stimulation in luteal cells obtained from mid-corpus luteum (CL) and
- the study of apoptosis induction and intracellular caspase-3 assay in human cells.
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
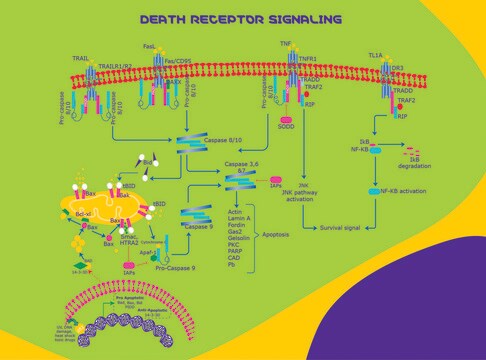
FASLG (Fas ligand) and Fas receptor constitute the basic elements in apoptosis. Interaction of FASLG with Fas receptor leads to activation of caspase-8. This caspase in turn leads to activation of effector caspases such as caspase-3, -6 and -7. This cascade results in the hydrolysis of nuclear and cytoplasmic components. Expression of FASLG is induced by nuclear factor-κB (NFκB). NFκB/FASLG pathway facilitates the suppression of p,p′-DDT (dichlorodiphenoxytrichloroethane)-induced cell toxicity by vitamin C and E. In CD4+ T cells, this protein is expressed on stimulus by T-cell receptor (TCR), both during normal and pathological conditions, such as alcohol exposure.
Fas ligand, a protein belonging to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family of cytokines, induces apoptosis in cells expressing the cell membrane receptor Fas (CD95/Apo-1).
Protein belonging to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family of cytokines; induces apoptosis in cells expressing the cell membrane receptor Fas (CD95/Apo-1).
Autres remarques
Human Fas Ligand, N-terminal 6X histidine-tagged, encodes amino acids 134-281.
Forme physique
Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in phosphate buffered saline containing 0.5 mg bovine serum albumin.
Remarque sur l'analyse
Measured by its ability to induce apoptosis in Jurkat cells.
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Malavika S Giri et al.
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950), 182(7), 4459-4470 (2009-03-21)
Mechanisms that may allow circulating monocytes to persist as CD4 T cells diminish in HIV-1 infection have not been investigated. We have characterized steady-state gene expression signatures in circulating monocytes from HIV-infected subjects and have identified a stable antiapoptosis gene
Xiaoting Jin et al.
PloS one, 9(12), e113257-e113257 (2014-12-03)
Dichlorodiphenoxytrichloroethane (DDT) is a known persistent organic pollutant and liver damage toxicant. However, there has been little emphasis on the mechanism underlying liver damage toxicity of DDT and the relevant effective inhibitors. Hence, the present study was conducted to explore
Aleksander Szymanowski et al.
Atherosclerosis, 233(2), 616-622 (2014-02-19)
Apoptosis of natural killer (NK) cells is increased in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) and may explain why NK cell levels are altered in these patients. Soluble forms of Fas and Fas ligand (L) are considered as markers of
Antonio M Galvao et al.
Biology of reproduction, 83(6), 901-908 (2010-08-20)
Proapoptotic factor Fas ligand (FASL) and its cell surface receptor FAS are tumor necrosis factor superfamily members that trigger apoptosis in different cell types. However, their influence on luteal steroidogenesis is not clearly understood. The aim of the present work
Intracellular bacteria engage a STING-TBK1-MVB12b pathway to enable paracrine cGAS-STING signalling.
Ramya Nandakumar et al.
Nature microbiology, 4(4), 701-713 (2019-02-26)
The innate immune system is crucial for eventual control of infections, but may also contribute to pathology. Listeria monocytogenes is an intracellular Gram-positive bacteria and a major cause of food-borne disease. However, important knowledge on the interactions between L. monocytogenes
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique