C8753
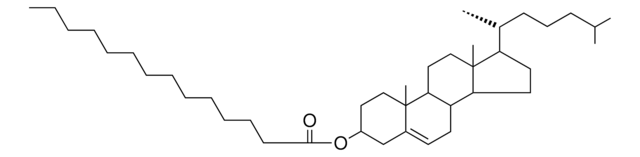
Cholesteryl arachidonate
≥95% (HPLC; detection at 205 nm), viscous liquid
Synonyme(s) :
3β-Hydroxy-5-cholestene 3-arachidonate, 5-Cholesten-3β-ol 3-arachidonate, Cholesteryl eicosatetraenoate
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Essai
≥95% (HPLC; detection at 205 nm)
Forme
viscous liquid
Couleur
clear
Groupe fonctionnel
ester
Conditions d'expédition
dry ice
Température de stockage
−20°C
Chaîne SMILES
CCCCC\C=C\C\C=C\C\C=C\C\C=C\CCCC(=O)OC1CCC2(C)C3CCC4(C)C(CCC4C3CC=C2C1)C(C)CCCC(C)C
InChI
1S/C47H76O2/c1-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18-19-20-21-22-23-27-45(48)49-40-32-34-46(5)39(36-40)28-29-41-43-31-30-42(38(4)26-24-25-37(2)3)47(43,6)35-33-44(41)46/h11-12,14-15,17-18,20-21,28,37-38,40-44H,7-10,13,16,19,22-27,29-36H2,1-6H3/b12-11+,15-14+,18-17+,21-20+
Clé InChI
IMXSFYNMSOULQS-SXXSVFILSA-N
Application
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Notes préparatoires
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Articles
Cholesterol undergoes esterification to improve transport. Cholesterol esters are more easily packaged into the interior of lipoproteins - increasing the quantity that can be readily transported in the blood stream.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique