A6781
Acetate Kinase from Bacillus stearothermophilus
lyophilized powder, 400-1,200 units/mg solid
Synonyme(s) :
ATP:Acetate phosphotransferase, Acetate Kinase Bacillus stearothermophilus
Se connecterpour consulter vos tarifs contractuels et ceux de votre entreprise/organisme
About This Item
Numéro CAS:
Numéro MDL:
Code UNSPSC :
12352204
eCl@ss :
32160410
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
bacterial (Bacillus stearothermophilus)
Niveau de qualité
Forme
lyophilized powder
Activité spécifique
400-1,200 units/mg solid
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Application
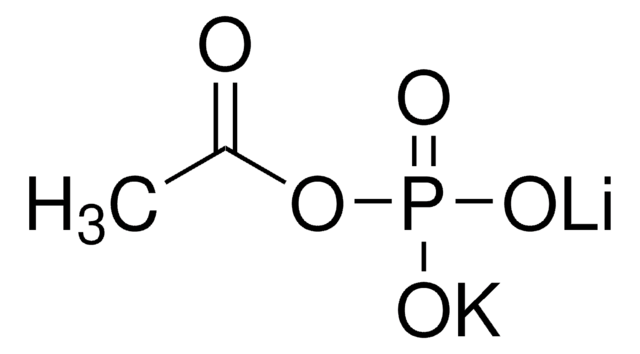
Acetate kinase is used to phosphorylate acetate to acetyl phosphate. Acetate Kinase from Bacillus stearothermophilus has been used to study allosteric activation. [32P]-acetyl phosphate was generated by incubating potassium acetate in the reaction mixture with acetate kinase from Sigma. This [32P]-acetyl phosphate was used to label BldM, BldM D-54N or BldM D-54A loci during the study of the effect of bldM gene on Streptomyces coelicolor development.
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Acetate kinase plays an important role in glycolysis. Acetate kinase phosphorylates acetate in the presence of ATP and a divalent cation, which ultimately results in the production of acetyl-CoA. Acetate kinase is also involved in the metabolism of propanoate, pyruvate and taurine. Acetate Kinase from Bacillus stearothermophilus is a thermostable tetramer of identical subunits with molecular weight of 40,000 Da each. The enzyme does not have a -SH group and is composed of 36% β-structure, 21 % α-helix and 43 % unordered structure.
Involved in the metabolism of propanoate, pyruvate and taurine.
Définition de l'unité
One unit will phosphorylate 1.0 μmole of acetate to acetyl phosphate per min at pH 7.2 at 30 °C.
Forme physique
Contains Tris-HCl buffer.
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Met. Corr. 1
Code de la classe de stockage
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
H Nakajima et al.
Journal of biochemistry, 86(5), 1169-1177 (1979-11-01)
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (FBP) stimulates the reaction of Bacillus stearothermophilus acetate kinase (AK). FBP changes the reaction curve for ATP from a sigmoidal type to a Michaelis-Menten one. The binding of FBP to AK was studied by an equilibrium dialysis method
F J Grundy et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 175(22), 7348-7355 (1993-11-01)
The Bacillus subtilis gene encoding acetate kinase was identified on the basis of sequence similarity to the Escherichia coli ackA gene and to a second E. coli gene closely related to ackA. Insertional inactivation of this region of the B.
V Molle et al.
Molecular microbiology, 36(6), 1265-1278 (2000-08-10)
whiK was one of five new whi loci identified in a recent screen of NTG-induced whi mutants and was defined by three mutants, R273, R318 and R655. R273 and R318 produce long, tightly coiled aerial hyphae with frequent septation. In
H Nakajima et al.
Journal of biochemistry, 84(1), 193-203 (1978-07-01)
1. Acetate kinase [EC 2.7.2.1] from an thermophile, B. stearothermophilus, was purified and crystalized. 2. This enzyme was shown to be a tetramer of identical subunits which had a molecular weight of about 40,000. Amino acid analysis showed no SH
Smirla Ramos-Montañez et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 192(24), 6390-6400 (2010-10-19)
Acetyl phosphate (AcP) is a small-molecule metabolite that can act as a phosphoryl group donor for response regulators of two-component systems (TCSs). The serious human respiratory pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) synthesizes AcP by the conventional pathway involving phosphotransacetylase and acetate
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique