A3281
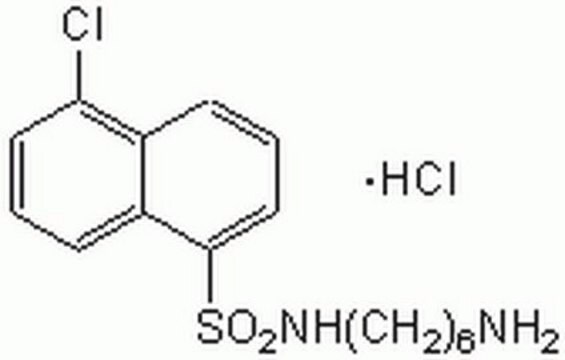
N-(6-Aminohexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalenesulfonamide hydrochloride
Synonyme(s) :
W-7
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Forme
powder
Mode d’action
cell membrane | interferes
enzyme | inhibits
Température de stockage
−20°C
Chaîne SMILES
Cl[H].NCCCCCCNS(=O)(=O)c1cccc2c(Cl)cccc12
InChI
1S/C16H21ClN2O2S.ClH/c17-15-9-5-8-14-13(15)7-6-10-16(14)22(20,21)19-12-4-2-1-3-11-18;/h5-10,19H,1-4,11-12,18H2;1H
Clé InChI
OMMOSRLIFSCDBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Informations sur le gène
human ... CAMK2A(815) , CAMK2B(816)
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Application
Actions biochimiques/physiologiques
Caractéristiques et avantages
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Contenu apparenté
Cyclic nucleotides, including cyclic AMP (cAMP), cyclic GMP (cGMP) and cyclic ADP-ribose, have been extensively studied as second messengers of intracellular events initiated by activation of GPCRs. cAMP modifies cell function in all eukaryotic cells, principally through the activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA), but also through cAMP-gated ion channels and guanine nucleotide exchange factors directly activated by cAMP.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique