91957
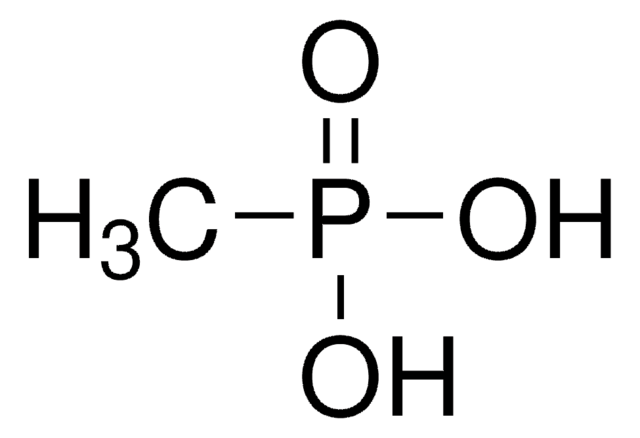
Monosodium methylphosphonate
99.0-101.0% (T)
Synonyme(s) :
Methanephosphonic acid monosodium salt, Methylphosphonic acid monosodium salt
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Pureté
99.0-101.0% (T)
Forme
crystals
Concentration
18.5-20.5% Na
Perte
≤2.0% loss on drying
pH
4.5-5.1
Solubilité
water: 3.54 g/30 mL, colorless
Traces de cations
Al: ≤5 mg/kg
Ba: ≤5 mg/kg
Bi: ≤5 mg/kg
Ca: ≤50 mg/kg
Cd: ≤5 mg/kg
Co: ≤5 mg/kg
Cr: ≤5 mg/kg
Cu: ≤5 mg/kg
Fe: ≤5 mg/kg
K: ≤50 mg/kg
Li: ≤5 mg/kg
Mg: ≤5 mg/kg
Mn: ≤5 mg/kg
Mo: ≤5 mg/kg
Ni: ≤5 mg/kg
Pb: ≤5 mg/kg
Sr: ≤5 mg/kg
Zn: ≤5 mg/kg
Absorption UV
λ: 260 nm Amax: ≤0.2
λ: 280 nm Amax: ≤0.07
Adéquation
no residue for filter test
Chaîne SMILES
O=P(C)(O[Na])O
InChI
1S/CH5O3P.Na/c1-5(2,3)4;/h1H3,(H2,2,3,4);/q;+1/p-1
Clé InChI
CZVWTNTXBUVAFR-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Application
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B
Code de la classe de stockage
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique