D27802
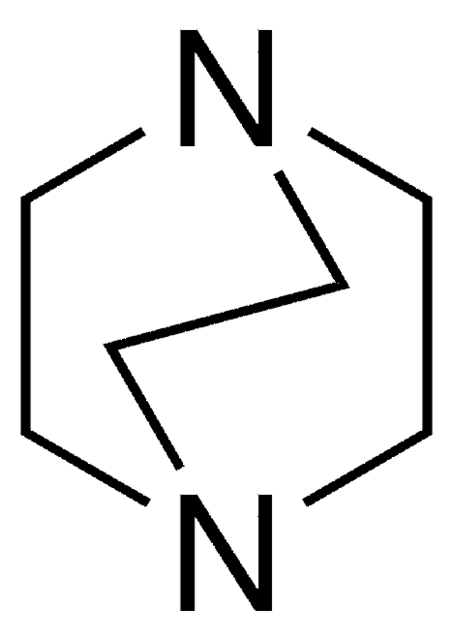
1,4-Diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane
ReagentPlus®, ≥99%
Synonyme(s) :
TED, Triethylenediamine
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Pression de vapeur
2.9 mmHg ( 50 °C)
Niveau de qualité
Gamme de produits
ReagentPlus®
Essai
≥99%
Forme
crystals
Caractéristiques du produit alternatif plus écologique
Catalysis
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
Indice de réfraction
n20/D 1.4634 (lit.)
Pf
156-159 °C (lit.)
Densité
1.02 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Autre catégorie plus écologique
, Aligned
Chaîne SMILES
N12CCN(CC2)CC1
InChI
1S/C6H12N2/c1-2-8-5-3-7(1)4-6-8/h1-6H2
Clé InChI
IMNIMPAHZVJRPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
We are committed to bringing you Greener Alternative Products, which adhere to one or more of The 12 Principles of Greener Chemistry. This product has been enhanced for catalytic efficiency. Click here for more information.
Application
- DABCO bis(perhydrate)
- DABCO monohydrate
- DABCO hexahydrate
Informations légales
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Sol. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2
Code de la classe de stockage
4.1B - Flammable solid hazardous materials
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
144.0 °F - closed cup
Point d'éclair (°C)
62.2 °C - closed cup
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique![1,8-Diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undéc-7-ène 98%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/120/564/5b373e23-1624-489c-8efb-692de0f96ffb/640/5b373e23-1624-489c-8efb-692de0f96ffb.png)

![1,4-Diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane for synthesis](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/images/488/587/f5a877b3-e573-4686-931f-648015f4d284/640/f5a877b3-e573-4686-931f-648015f4d284.jpg)

![1,5,7-Triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene 98%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/171/446/333d560c-cff6-4958-b489-5acfb3057cce/640/333d560c-cff6-4958-b489-5acfb3057cce.png)
![1,4-Diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane bis(sulfur dioxide) adduct ≥95% (sulfur, elemental analysis)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/158/739/a9df497b-883d-40f1-ac45-bf699dcee9f9/640/a9df497b-883d-40f1-ac45-bf699dcee9f9.png)



![1,5-Diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-5-ene 98%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/400/401/859b2474-712b-4448-b231-74d0bc3203f1/640/859b2474-712b-4448-b231-74d0bc3203f1.png)



![Bis[2-(N,N-dimethylamino)ethyl] ether 97%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/372/323/505a46ae-b067-4177-8e5f-19a3f4ef9c44/640/505a46ae-b067-4177-8e5f-19a3f4ef9c44.png)