MAB1618
Anticorps anti-dynéine, chaînes intermédiaires de 74 kDa, cytoplasmique, clone 74.1
clone 74.1, Chemicon®, from mouse
Synonyme(s) :
Cytoplasmic dynein 1 intermediate chain 1, Cytoplasmic dynein intermediate chain 1, Dynein intermediate chain 1, cytosolic, DH IC-1, Cytoplasmic dynein 1 intermediate chain 2, Cytoplasmic dynein intermediate chain 2, Dynein intermediate chain 2, cytosoli
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Source biologique
mouse
Niveau de qualité
Forme d'anticorps
purified antibody
Type de produit anticorps
primary antibodies
Clone
74.1, monoclonal
Espèces réactives
Xenopus, mouse, fish, rat, human, sheep, Drosophila, bovine
Ne doit pas réagir avec
squid
Fabricant/nom de marque
Chemicon®
Technique(s)
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunofluorescence: suitable
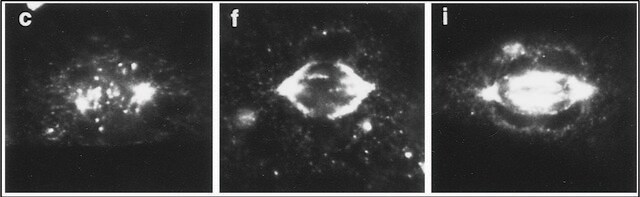
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
western blot: suitable
Isotype
IgG2b
Numéro d'accès NCBI
Conditions d'expédition
wet ice
Modification post-traductionnelle de la cible
unmodified
Informations sur le gène
human ... DYNC1I1(1780)
Description générale
Spécificité
Application
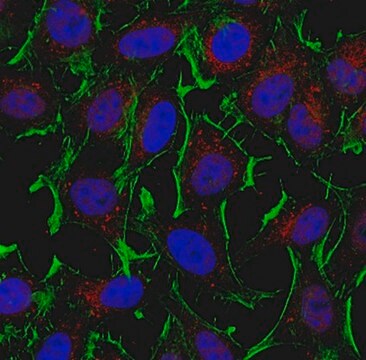
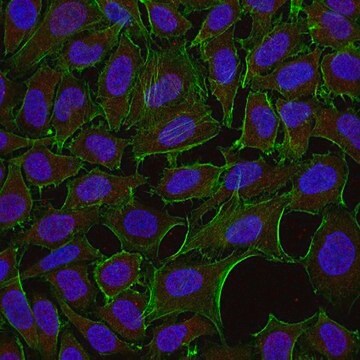
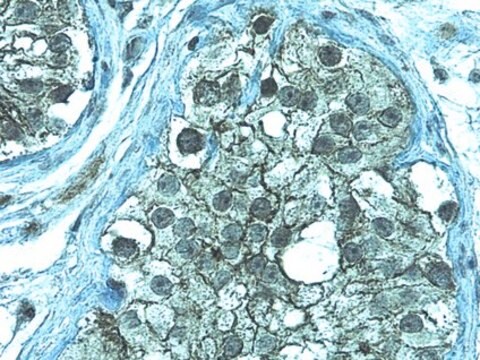
une dilution au 1/50e-1/100e d'un lot antérieur a été utilisée. Réagit avec des cellules MDCK, NRR, N1E, et PTK-1 mises en culture.
Immunoprécipitation :
10 µl d'un précédent lot ont été utilisés pour 0,5 gm de tissus. L'anticorps monoclonal immunoprécipite proprement l'ensemble du complexe dynéine de façon stœchiométrique à partir de lysats TX-100 ou NP-40 (comprenant la chaîne lourde de 530 kD, les chaînes intermédiaires légères et les chaînes légères) de divers tissus et lignées cellulaires mises en culture. Si l'on utilise des produits détergents comme le SDS pour préparer les lysats, les seules sous-unités de la dynéine qui sont immunoprécipitées sont les sous-unités IC74 (vraisemblablement parce que le complexe dynéine se dissocie), et d'autres protéines contaminantes peuvent être observées dans les immunoprécipités de SDS.
Immunoblotting :
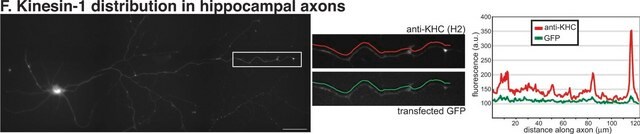
dilution au 1/1 000e-1/5 000e. Réagit avec des cellules MDCK, PC-12, N1E, des neurones, des cellules gliales et d'autres cellules mises en culture.
Il revient à l'utilisateur final de déterminer les dilutions de travail optimales.
Qualité
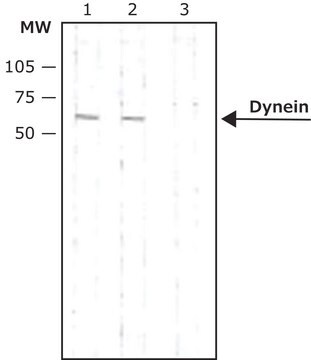
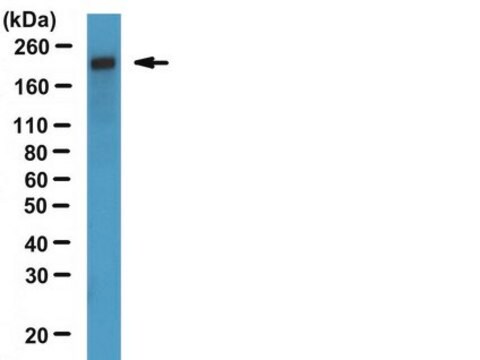
Analyse par western blotting :
une dilution au 1/500e de ce lot a permis de détecter la DYNÉINE dans 10 µg de lysat de cellules A431.
Description de la cible
Forme physique
Remarque sur l'analyse
Cellules HeLa, lysat de cellules A431
Autres remarques
Informations légales
Vous ne trouvez pas le bon produit ?
Essayez notre Outil de sélection de produits.
En option
Code de la classe de stockage
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique