T11509
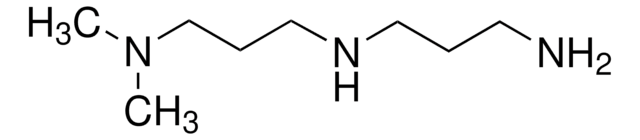
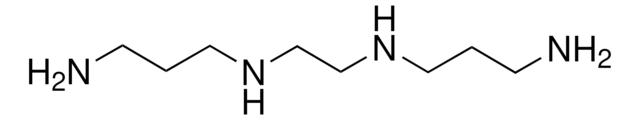
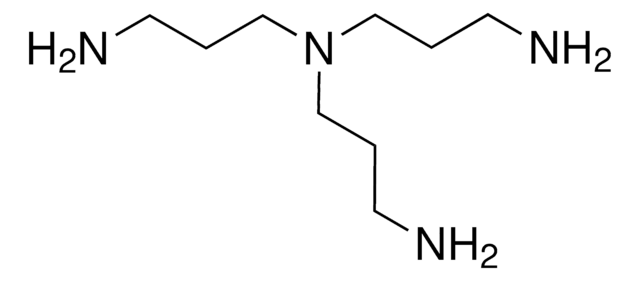
Tetraethylenepentamine
technical grade
Synonyme(s) :
TEPA, Tetrene
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Qualité
technical grade
Niveau de qualité
Densité de vapeur
6.53 (vs air)
Pression de vapeur
<0.01 mmHg ( 20 °C)
Température d'inflammation spontanée
610 °F
Indice de réfraction
n20/D 1.505 (lit.)
pb
340 °C
Pf
−40 °C (lit.)
Densité
0.998 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Chaîne SMILES
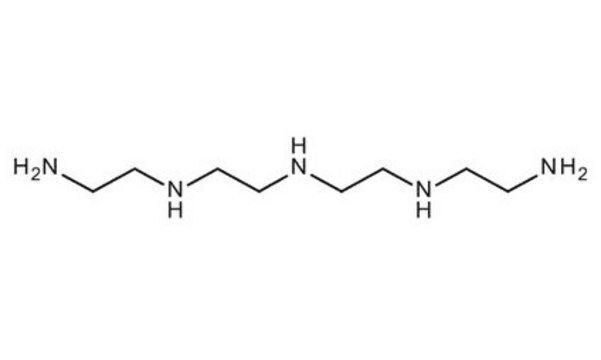
NCCNCCNCCNCCN
InChI
1S/C8H23N5/c9-1-3-11-5-7-13-8-6-12-4-2-10/h11-13H,1-10H2
Clé InChI
FAGUFWYHJQFNRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Catégories apparentées
Description générale
Application
- To functionalize magnesium 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalate (Mg-MOF-74) to enhance the CO2 adsorption performance of the material.
- To modify magnetic chitosan resin to form amine-bearing chitosan for the efficient removal of uranium from an aqueous solution.
- To synthesize poly(vinyl-chloride)/tetraethylenepentamine (PVC-TEPA) composite material, which is used as an efficient catalyst for the Knoevenagel condensation reaction.
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1B - Skin Sens. 1
Code de la classe de stockage
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 2
Point d'éclair (°F)
325.4 °F - closed cup
Point d'éclair (°C)
163 °C - closed cup
Équipement de protection individuelle
Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique