777048
2-[(7-{4-[N,N-Bis(4-methylphenyl)amino]phenyl}-2,1,3-benzothiadiazol-4-yl)methylene]propanedinitrile
97% (HPLC)
Synonyme(s) :
DTDCPB
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Pureté
97% (HPLC)
Forme
powder
Pf
285-290 °C
λmax
570 nm in dichloromethane
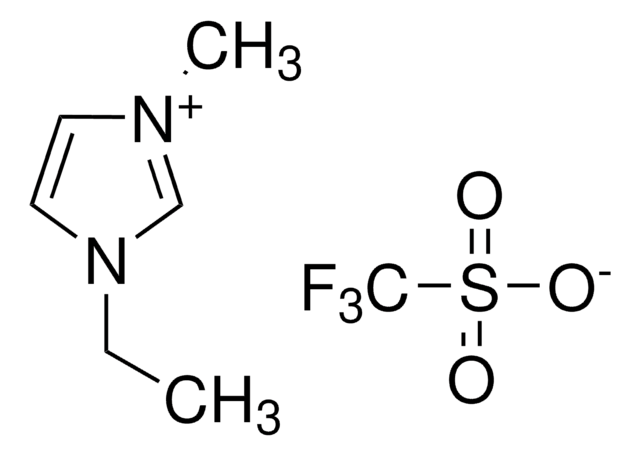
Chaîne SMILES
Cc1ccc(cc1)N(c2ccc(C)cc2)c3ccc(cc3)-c4ccc(\C=C(/C#N)C#N)c5nsnc45
InChI
1S/C30H21N5S/c1-20-3-10-25(11-4-20)35(26-12-5-21(2)6-13-26)27-14-7-23(8-15-27)28-16-9-24(17-22(18-31)19-32)29-30(28)34-36-33-29/h3-17H,1-2H3
Clé InChI
METIWNNPHPBEHP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Description générale
Application
A vacuum-deposited organic solar cell employing this novel donor-acceptor-acceptor (D-A-A) donor molecule; DTDCPB; combined with the electron acceptor C60/ C70 achieved a record-high power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 6.8%.
Device structure:
MoO3 (30nm) / DTDCPB (7nm) / DTDCPB:C70 (40nm) / C70 (7nm) / BCP (10nm) / Ag (150nm)
Device performance:
- JSC = 13.48 mA/cm2
- VOC = 0.95 V
- FF = 0.55
- PCE = 6.8%
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Organes cibles
Respiratory system
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Vous ne trouvez pas la bonne version ?
Si vous avez besoin d'une version particulière, vous pouvez rechercher un certificat spécifique par le numéro de lot.
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Articles
Solution-processed organic photovoltaic devices (OPVs) have emerged as a promising clean energy generating technology due to their ease of fabrication, potential to enable low-cost manufacturing via printing or coating techniques, and ability to be incorporated onto light weight, flexible substrates.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique