736236
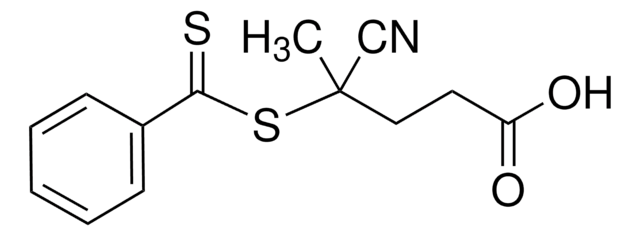
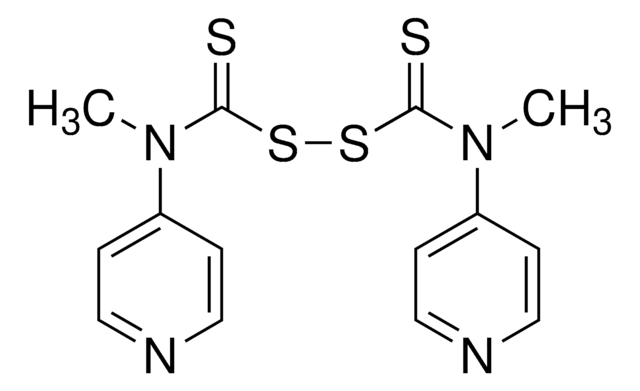
2-Cyanopropan-2-yl N-methyl-N-(pyridin-4-yl)carbamodithioate
97% (HPLC)
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Pureté
97% (HPLC)
Forme
solid
Pf
97-102 °C
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Chaîne SMILES
CN(C(=S)SC(C)(C)C#N)c1ccncc1
InChI
1S/C11H13N3S2/c1-11(2,8-12)16-10(15)14(3)9-4-6-13-7-5-9/h4-7H,1-3H3
Clé InChI
PYVIBYAVTHICFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Application
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Sens. 1
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Vous ne trouvez pas la bonne version ?
Si vous avez besoin d'une version particulière, vous pouvez rechercher un certificat spécifique par le numéro de lot.
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Universal (Switchable) RAFT agents allow for the polymerization of both less activated and more activated monomers and are ideal for the synthesis of well-defined block copolymers.
A series of polymerization were carried out using RAFT agents and monomers yielding well-defined polymers with narrow molecular weight distributions. The process allows radical-initiated growing polymer chains to degeneratively transfer reactivity from one to another through the use of key functional groups (dithioesters, trithiocarbonates, xanthates and dithiocarbamates). RAFT agents help to minimize out-of-control growth and prevent unwanted termination events from occurring, effectively controlling polymer properties like molecular weight and polydispersity. RAFT agents are commercially available. RAFT does not use any cytotoxic heavy metal components (unlike ATRP).
The modification of biomacromolecules, such as peptides and proteins, through the attachment of synthetic polymers has led to a new family of highly advanced biomaterials with enhanced properties.
We presents an article about a micro review of reversible addition/fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. RAFT (Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer) polymerization is a reversible deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) and one of the more versatile methods for providing living characteristics to radical polymerization.
Protocoles
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
We present an article about RAFT, or Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer, which is a form of living radical polymerization.
An article about the typical procedures for polymerizing via ATRP, which demonstrates that in the following two procedures describe two ATRP polymerization reactions as performed by Prof. Dave Hadddleton′s research group at the University of Warwick.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique

![4-Cyano-4-[(dodecylsulfanylthiocarbonyl)sulfanyl]pentanoic acid 97% (HPLC)](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/204/925/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af/640/30ae6ca0-5b0b-4963-a061-7e5e3d1a85af.png)