730807
Silver, dispersion
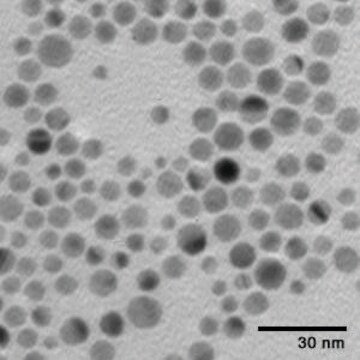
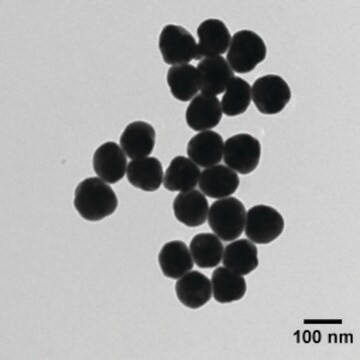
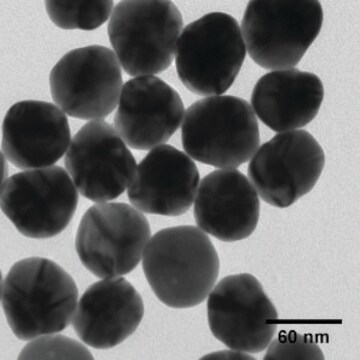
nanoparticles, 40 nm particle size (TEM), 0.02 mg/mL in aqueous buffer, contains sodium citrate as stabilizer
Synonyme(s) :
Colloidal silver
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Forme
nanoparticles
Niveau de qualité
Contient
sodium citrate as stabilizer
Concentration
0.02 mg/mL in aqueous buffer
Indice de réfraction
n20/D 1.333
Taille des particules
40 nm (TEM)
Densité
0.990 g/mL at 25 °C
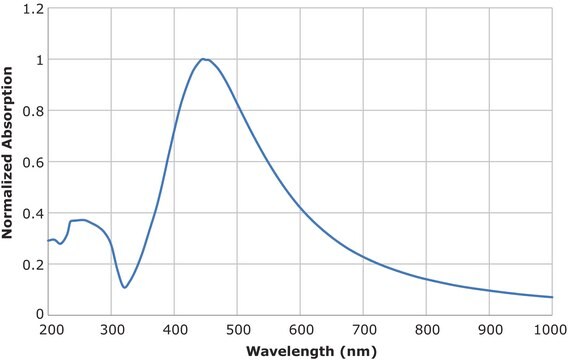
Fluorescence
λem 412 nm FWHM 63 nm
Température de stockage
2-8°C
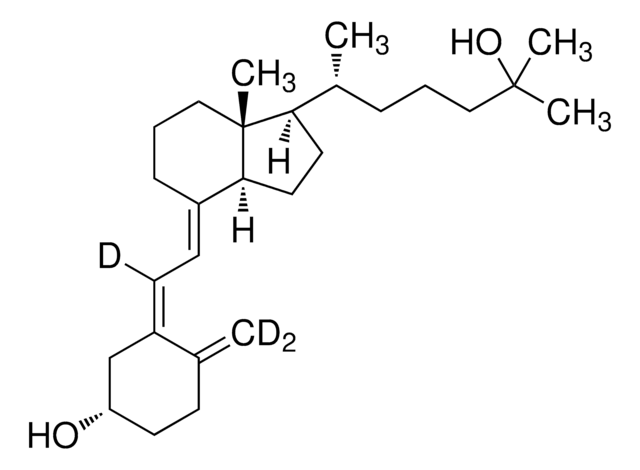
Chaîne SMILES
[Ag]
InChI
1S/Ag
Clé InChI
BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Catégories apparentées
Description générale
Application
- Silver as acrolein hydrogenation catalyst: intricate effects of catalyst nature and reactant partial pressures.: This study explores the use of silver as a catalyst for acrolein hydrogenation, highlighting the complex effects of catalyst nature and the partial pressures of reactants, which could inform future applications in industrial chemical processes (Bron et al., 2007).
- Surface-enhanced Raman analysis of sulfa drugs on colloidal silver dispersion.: This research discusses the application of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) using colloidal silver dispersions for analyzing sulfa drugs, potentially enhancing detection methods in pharmaceutical research (Sutherland et al., 1990).
Mention d'avertissement
Warning
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1
Code de la classe de stockage
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Articles
A key challenge for nanomaterial safety assessment is the ability to handle the large number of newly engineered nanomaterials (ENMs), including developing cost-effective methods that can be used for hazard screening.
Silver nanomaterials have unique physical, chemical, and optical properties that are currently being leveraged for a wide variety of biological applications.
Advances in materials have often been led by the development of new synthetic methods that provide control over size, morphology and structure.
Advances in materials have often been led by the development of new synthetic methods that provide control over size, morphology and structure. The preparation of materials in a scalable and continuous manner is critical when development moves beyond lab-scale quantities.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique