704105
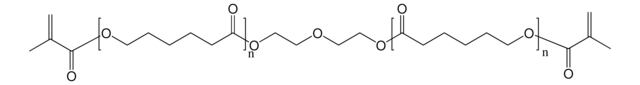
Polycaprolactone
average Mn 45,000
Synonyme(s) :
Homopolymère de 2-oxépanone, Polymère de 6-caprolactone
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Forme
pellets
Niveau de qualité
Indice de fusion
1.8 g/10 min (80 °C, 44 psi)
Poids mol.
Mn 40,000-50,000
Mw 48,000-90,000
average Mn 45,000
Pf
56-64 °C
60 °C (lit.)
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
Caractéristiques et avantages
Non toxique, biodégradable dans le sol, large miscibilité, compatibilité mécanique avec de nombreux polymères, et bonne adhérence à un large spectre de substrats.
Produit(s) apparenté(s)
Code de la classe de stockage
11 - Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 3
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Certificats d'analyse (COA)
Recherchez un Certificats d'analyse (COA) en saisissant le numéro de lot du produit. Les numéros de lot figurent sur l'étiquette du produit après les mots "Lot" ou "Batch".
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
We will explore the technological advances that have contributed toward the progress of 3DP of tissue engineering scaffolds, current materials used to create 3DP scaffolds, and the challenges that remain.
In the past two decades, tissue engineering and regenerative medicine have become important interdisciplinary fields that span biology, chemistry, engineering, and medicine.
Innovations in polymer technology have had a significant impact on the advancement of novel drug delivery systems.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique





![Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid] natural origin](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/129/476/7d1c924b-f644-4889-a2d6-d7a923ce382c/640/7d1c924b-f644-4889-a2d6-d7a923ce382c.png)